Forests
The Main Factors That Contribute to Forest Destruction
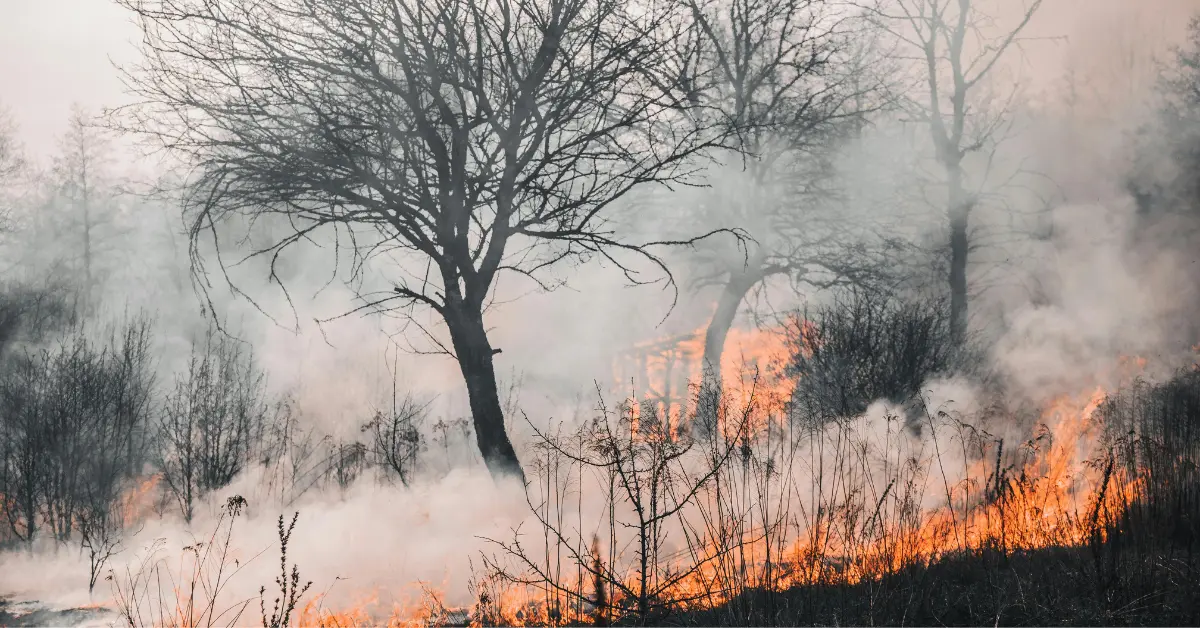

Key Takeaways
- Forest destruction is a major global issue driven by human activities and natural causes.
- Agricultural expansion, logging, urbanization, and climate change are the leading causes.
- Understanding these factors is the first step toward protecting forests.
- Practical solutions include sustainable farming, reforestation, and policy enforcement.
What is Causing Forest Destruction?
Forests are one of the planet’s most vital ecosystems. They provide us with clean air, regulate the climate, and house countless species of wildlife. Yet, these natural havens are vanishing at an alarming rate. You might wonder: What’s really driving this destruction? Let’s dive deep into the causes.
Agricultural Expansion
Agriculture is the biggest culprit when it comes to forest destruction. Farmers clear vast areas of forest to grow crops or raise livestock. This happens in two main ways.
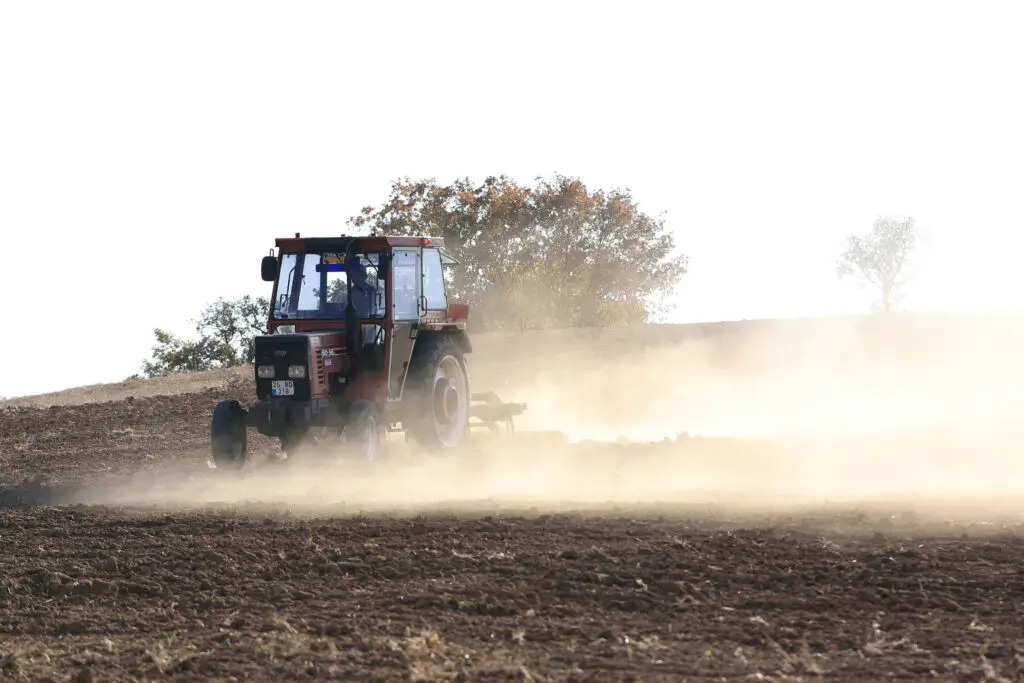

Commercial Farming
Large-scale operations, like growing palm oil, soy, and other cash crops, often require cutting down entire forests. For example, the Amazon Rainforest has lost significant portions to soybean plantations.

Subsistence Farming
In developing countries, many small-scale farmers use slash-and-burn methods to clear land for crops. While it helps them survive, it severely damages ecosystems and leads to long-term soil depletion.

Logging Activities
Logging is another major factor. Wood is essential for furniture, paper, and construction, but how it’s sourced makes a huge difference.

Legal Logging
Commercial logging, when done responsibly, can minimize harm. However, logging companies often exploit loopholes, cutting down more trees than allowed.

Illegal Logging
Illegal logging takes things further, causing irreversible harm. Rare species of trees are targeted, and the lack of regulation leads to excessive deforestation.

Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
As cities grow, forests shrink. Urbanization often comes at the cost of clearing land for housing, factories, and roads.

Building Roads and Cities
Expanding road networks into forested areas opens up land for settlements. It also paves the way for further deforestation by giving easier access to remote areas.

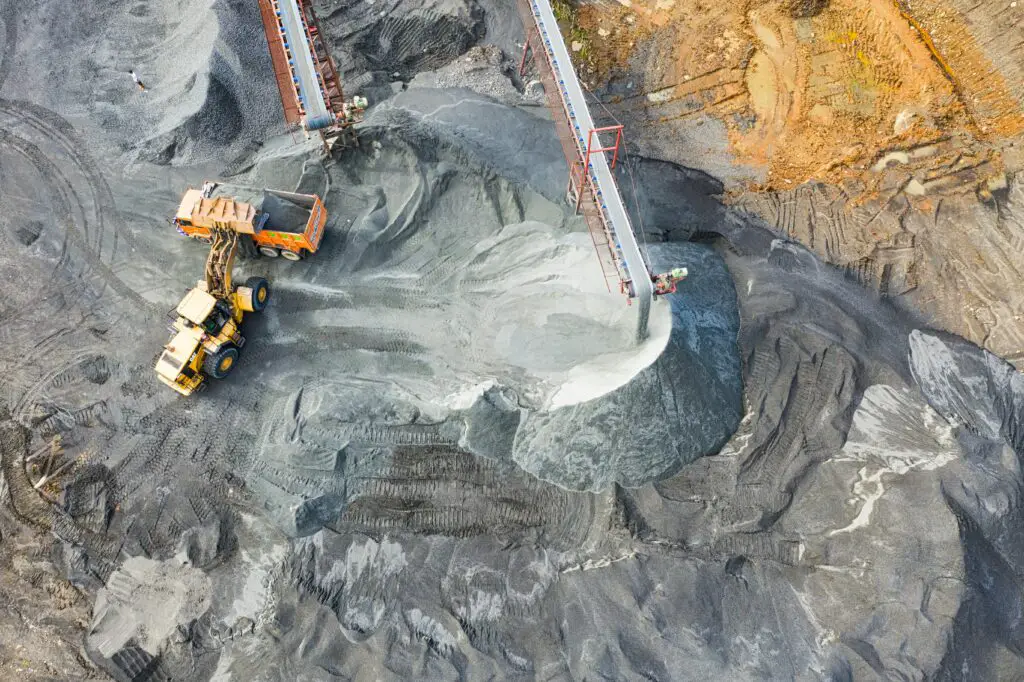
Mining and Industrial Projects
Mining for resources like gold, coal, and oil leads to large-scale destruction. Forests are cleared to set up mines, and toxic waste often damages surrounding ecosystems.

Climate Change and Natural Causes
You might not think of climate change as a direct cause, but it plays a big role.
Wildfires
Hotter, drier conditions caused by climate change make wildfires more frequent and intense. These fires destroy millions of acres of forest each year.
Feedback Loop
When forests are cut down, they release stored carbon, worsening global warming. This creates a vicious cycle where climate change and deforestation feed into each other.
Livestock Grazing and Overpopulation
Forests are often cleared to make way for grazing land. As demand for meat grows, so does the pressure to convert forests into pastures.
Overpopulation adds another layer to the problem. More people mean a higher demand for land, food, and resources, which puts forests in the firing line.
Industrial Exploitation
Industrial-scale plantations, like those for palm oil or rubber, lead to monocultures that replace diverse forest ecosystems. The loss of biodiversity in these areas is staggering, affecting everything from plants to animals.
What Can We Do to Stop It?
It’s not all doom and gloom. There are practical ways to slow down and even reverse forest destruction:
Reforestation and Afforestation
Planting trees can help restore degraded land. Large-scale initiatives like reforestation campaigns are already making a difference in some regions.
Sustainable Farming Practices
Agroforestry, where trees are grown alongside crops, is a sustainable alternative. It helps farmers maintain productivity while preserving biodiversity.
Stronger Policies and Regulations
Governments need to enforce stricter laws against illegal logging and deforestation. Incentives for sustainable land use can encourage businesses to adopt eco-friendly practices.
Community Engagement
Local communities play a vital role in forest conservation. Educating them about sustainable practices and involving them in decision-making processes can yield great results.
FAQs
Why is forest destruction such a big deal?
Forests are critical for absorbing carbon dioxide, supporting wildlife, and regulating the climate. Losing them has devastating effects on the environment and our quality of life.
What is the leading cause of forest destruction?
Agricultural expansion is the top driver, with commercial farming like palm oil and soy production leading the way.
Can we reverse forest destruction?
Yes, through reforestation, sustainable farming, and enforcing strict policies, we can restore damaged ecosystems and slow down deforestation.
Conclusion
Forest destruction is a complex issue, but understanding its causes is the first step to solving it. By addressing agricultural practices, illegal logging, urban expansion, and climate change, we can protect these vital ecosystems. Whether it’s planting a tree or supporting sustainable products, everyone has a role to play in saving our forests.
Let’s act before it’s too late. Forests aren’t just resources—they’re our lifeline.
Forests
The 10 Best Forests to Visit in the World

Key Takeaways
- Explore the breathtaking beauty of the world’s most famous forests.
- Learn about unique features, wildlife, and activities in each forest.
- Discover the best times to visit and what makes these forests stand out.
- Perfect guide for nature lovers, travelers, and eco-tourists.
Are you someone who finds peace walking among tall trees, breathing in the fresh earthy scent, and listening to the songs of birds? Forests are some of the most enchanting places on Earth. They’re not just about trees and greenery—they’re alive with unique ecosystems, history, and experiences you can’t find anywhere else.
In this article, we’ll take you through the 10 best forests to visit in the world, each offering a slice of magic. Let’s get started on this green adventure!
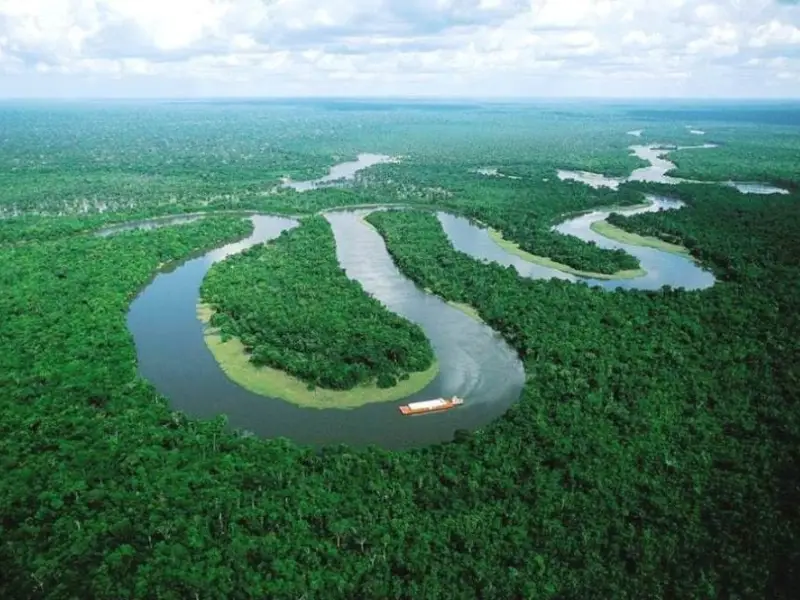
Amazon Rainforest, South America
The Amazon is often called the “lungs of the Earth,” and for a good reason. Spanning over nine countries, it’s the largest rainforest in the world.
- Why Visit: The Amazon is home to more than 10% of the world’s species, from jaguars to colorful parrots. It’s a dream for wildlife lovers.
- What to Do: Go on guided boat tours, hike jungle trails, or experience local Amazonian culture.
- Best Time to Visit: June to November (dry season).
- Interesting Fact: The Amazon produces 20% of the world’s oxygen.

Black Forest, Germany
The Black Forest isn’t just famous for its name—it’s the inspiration behind fairy tales by the Brothers Grimm.
- Why Visit: Rolling hills, thick woods, and charming villages make this a magical destination.
- What to Do: Hike along the Feldberg mountain, explore cuckoo clock workshops, or relax in thermal spas.
- Best Time to Visit: May to September for pleasant weather.
- Interesting Fact: It’s known for its Black Forest cake and ancient tales.
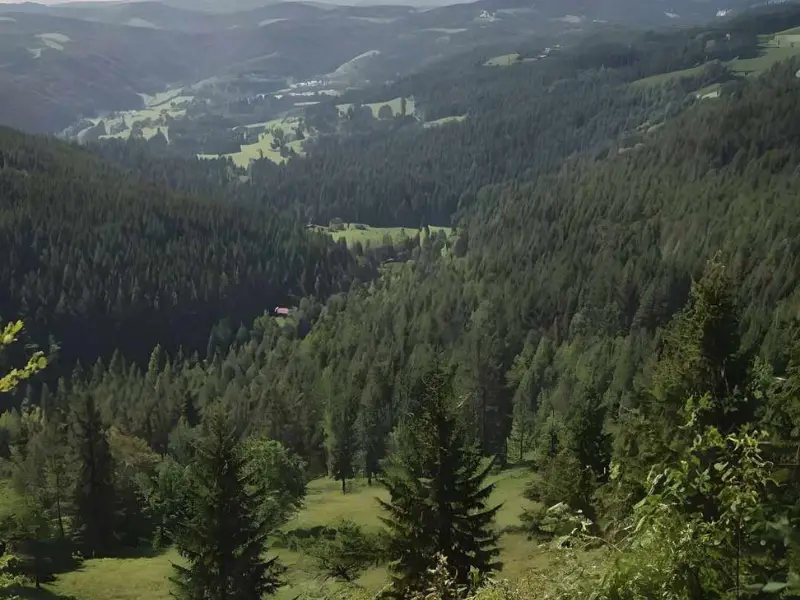

Daintree Rainforest, Australia
The Daintree is one of the oldest rainforests in the world, dating back 180 million years!
- Why Visit: Dense greenery, rare species like the cassowary, and stunning beaches nearby.
- What to Do: Explore on canopy walks, take a crocodile river cruise, or visit Cape Tribulation.
- Best Time to Visit: May to September (dry season).
- Interesting Fact: This forest inspired scenes from the movie “Avatar.”

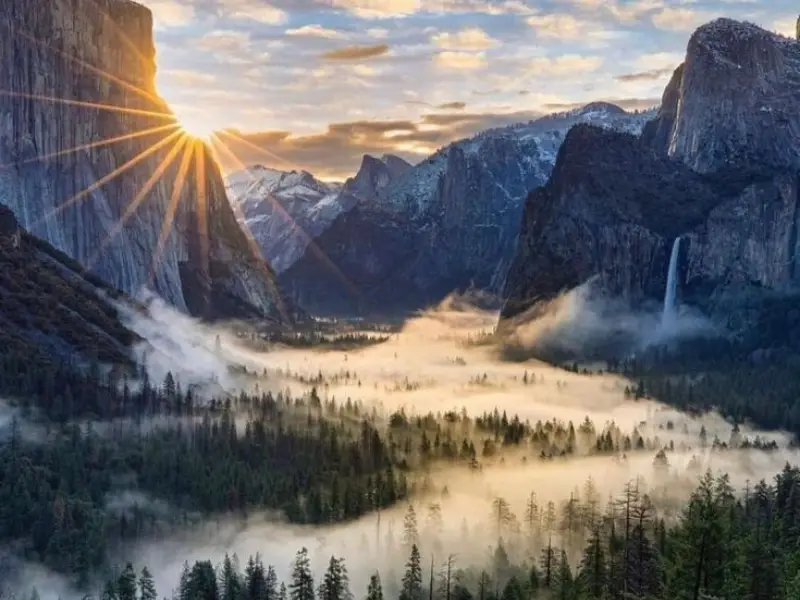
Yosemite National Park, USA
Yosemite is not just a forest—it’s a national treasure with granite cliffs, waterfalls, and giant sequoias.
- Why Visit: Perfect mix of towering trees and dramatic landscapes.
- What to Do: Camp, rock climb, or visit Glacier Point for jaw-dropping views.
- Best Time to Visit: Spring (April to June) for waterfalls or fall (September to November) for colors.
- Interesting Fact: Home to El Capitan, a favorite for climbers worldwide.

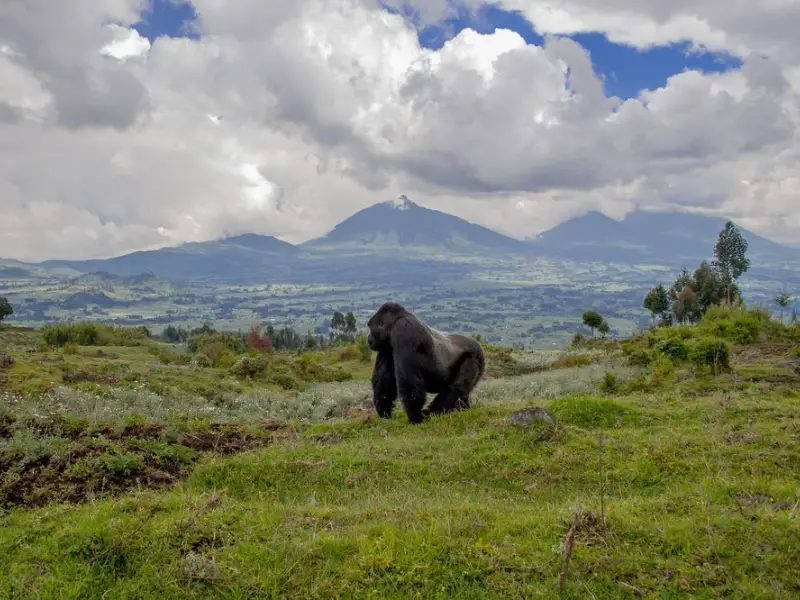
Bwindi Impenetrable Forest, Uganda
If you’ve ever dreamed of seeing gorillas in the wild, Bwindi is the place to go.
- Why Visit: A UNESCO World Heritage site with mountain gorillas and diverse flora.
- What to Do: Gorilla trekking is the highlight.
- Best Time to Visit: June to September or December to February.
- Interesting Fact: Nearly half of the world’s mountain gorillas live here.

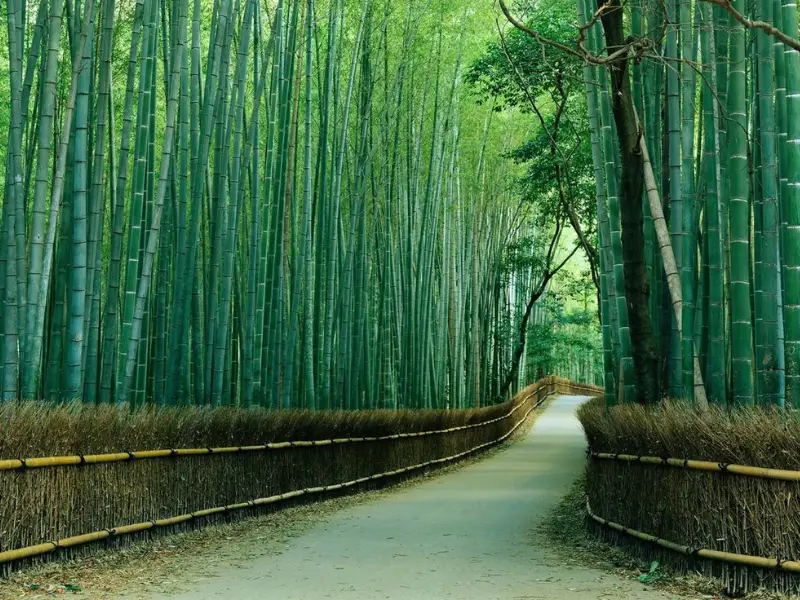
Sagano Bamboo Forest, Japan
Walking through this bamboo forest feels like stepping into another world.
- Why Visit: Unique bamboo groves with serene pathways.
- What to Do: Stroll through the forest and visit nearby temples.
- Best Time to Visit: Spring (March to May) or autumn (October to November).
- Interesting Fact: The sound of wind through the bamboo is considered a natural treasure in Japan.

Valdivian Temperate Rainforest, Chile
This rainforest is known for its ancient trees and cool, misty climate.
- Why Visit: Rare wildlife like the pudú (world’s smallest deer).
- What to Do: Hike, birdwatch, or explore the coastline.
- Best Time to Visit: December to February (summer).
- Interesting Fact: It’s one of the few temperate rainforests in the world.

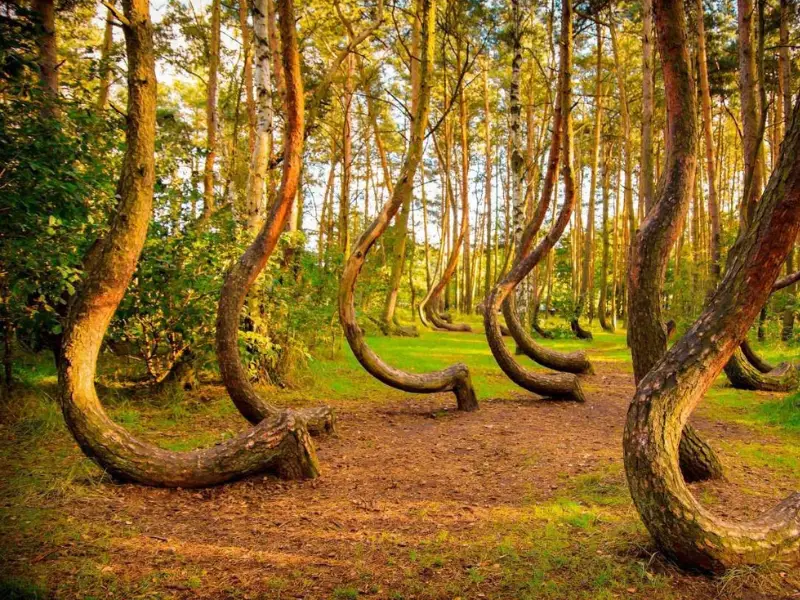
Crooked Forest, Poland
This small forest is famous for its oddly-shaped pine trees.
- Why Visit: A mysterious and photogenic destination.
- What to Do: Walk through the grove and learn about its unique history.
- Best Time to Visit: Spring or summer.
- Interesting Fact: The reason behind the curved trees is still debated.

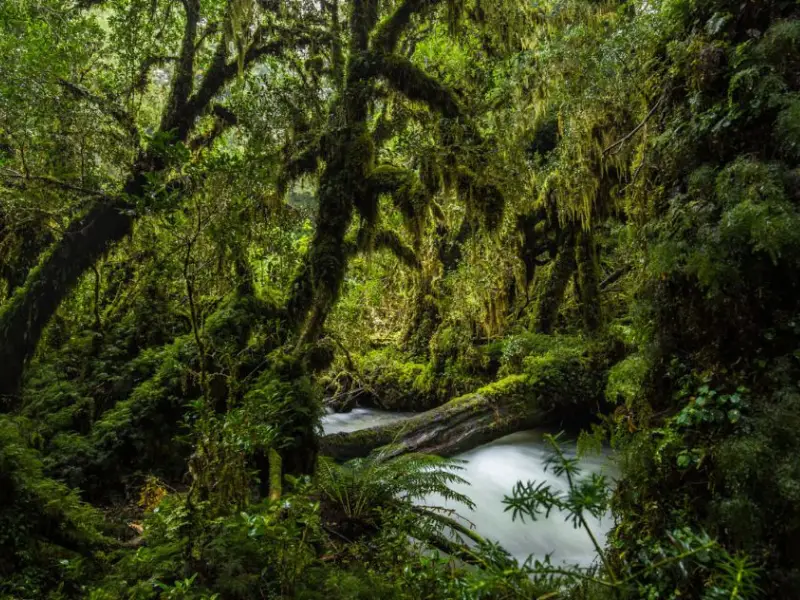
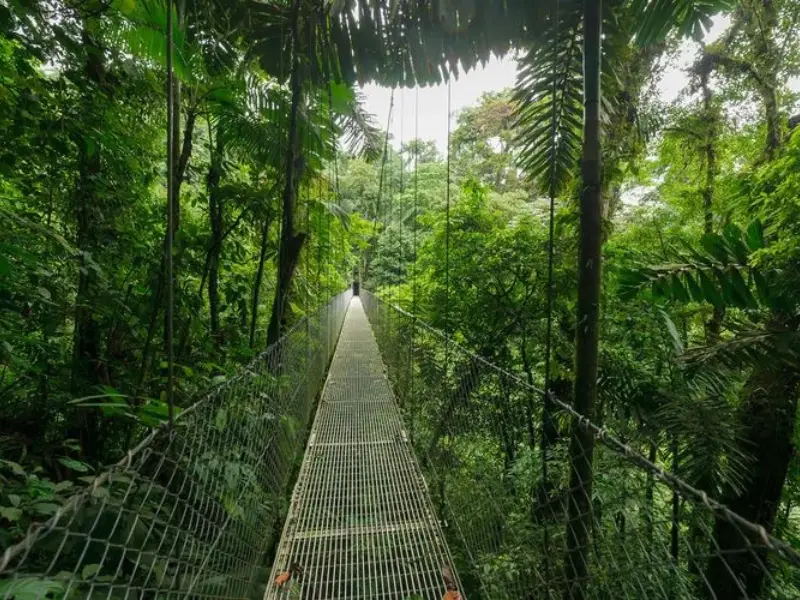
Monteverde Cloud Forest, Costa Rica
High up in the mountains, this cloud forest feels like a fairytale.
- Why Visit: Unique ecosystem shrouded in mist.
- What to Do: Walk canopy bridges, zip-line, or go birdwatching for quetzals.
- Best Time to Visit: November to April (dry season).
- Interesting Fact: Over 2,500 plant species grow here.

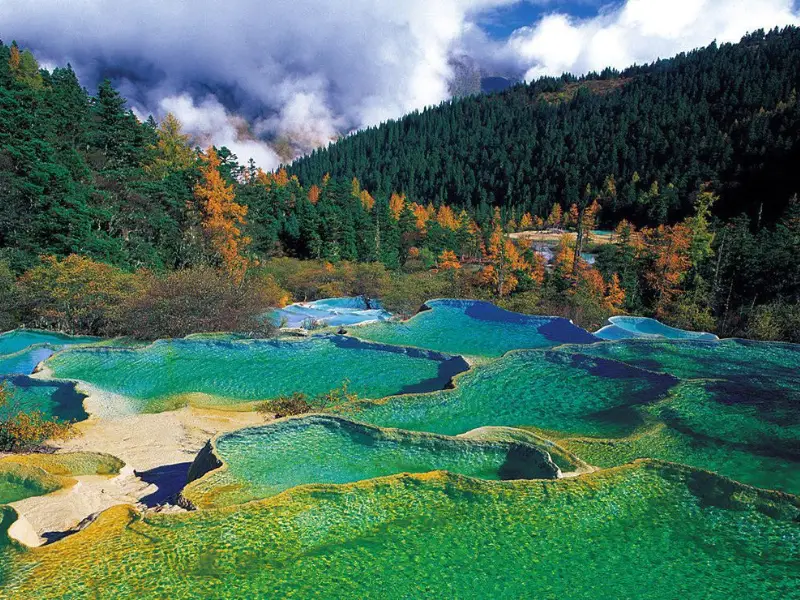
Jiuzhaigou Valley, China
Jiuzhaigou is a colorful paradise with turquoise lakes and snow-capped mountains.
- Why Visit: Stunning natural beauty with vibrant lakes and forests.
- What to Do: Hike, take photographs, or enjoy local Tibetan culture.
- Best Time to Visit: September to November for clear skies.
- Interesting Fact: It’s part of a UNESCO World Heritage site.

FAQs
Q: Which forest is the best for wildlife lovers?
A: The Amazon Rainforest and Bwindi Impenetrable Forest are ideal for spotting rare wildlife.
Q: Are these forests safe to visit?
A: Most forests have guided tours to ensure safety. Always follow local guidelines.
Q: What should I pack for a forest trip?
A: Comfortable shoes, weather-appropriate clothing, insect repellent, and water.
Conclusion
From the vast Amazon to the serene Sagano Bamboo Forest, the world is full of incredible forests waiting to be explored. Whether you’re into hiking, photography, or simply soaking up nature’s beauty, there’s a forest for you. So pack your bags, lace up your boots, and start exploring these green wonders!
By visiting these forests, you’re not just creating memories—you’re supporting efforts to preserve our planet’s most beautiful ecosystems.
Forests
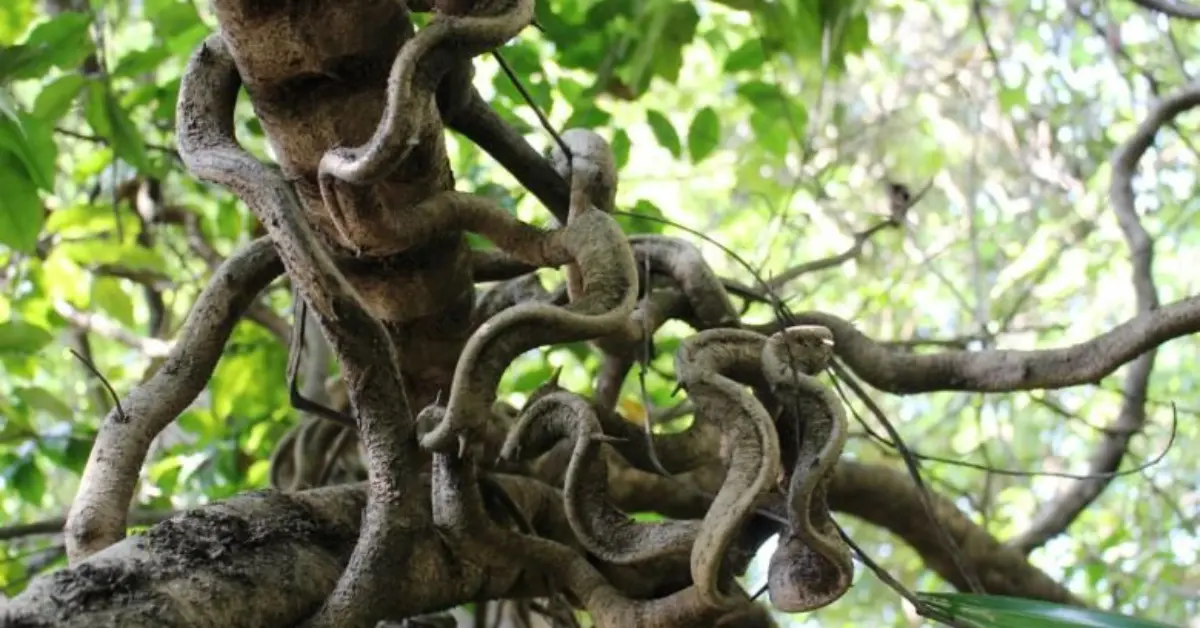
Large Vines That Grow in Forests: A Deep Dive into Nature’s Giants

Key Takeaways
- Large vines, like lianas and rattan, are essential parts of forest ecosystems.
- They serve roles such as supporting wildlife, maintaining soil stability, and contributing to the forest canopy.
- While beneficial, some vines can become invasive and harm native species.
- Understanding their growth patterns and types helps in preserving biodiversity and managing ecosystems effectively.
Introduction
Have you ever wandered through a dense forest and noticed thick, twisting vines weaving their way up trees and across the canopy? These are the large vines of the forest—nature’s climbers and connectors. From tropical rainforests to temperate woodlands, these incredible plants shape ecosystems, create habitats, and sometimes present challenges.
But what makes these vines so special? How do they grow, and why are they so important? Whether you’re a forest lover or just curious about nature’s marvels, this article breaks it all down for you in an easy-to-understand way. Let’s untangle the story of large forest vines!
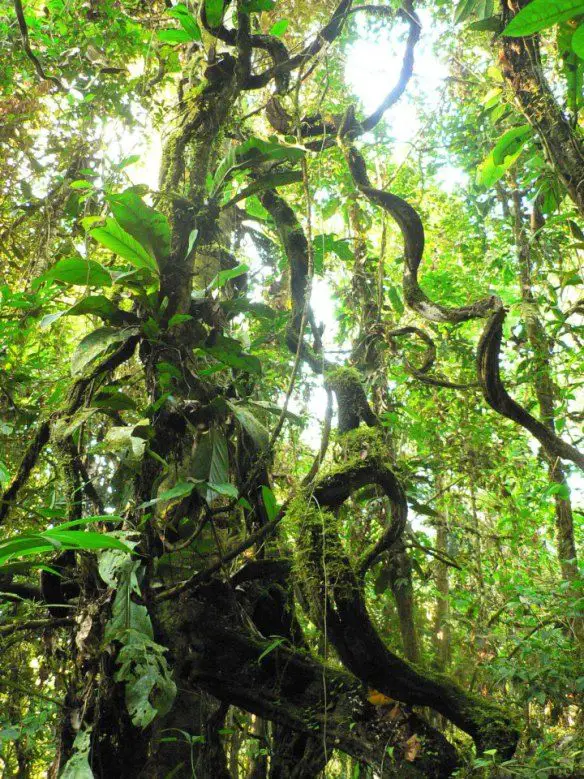

What Are Large Vines?
Large vines are long, climbing plants that grow in forests. Unlike trees, they don’t have a rigid trunk. Instead, they rely on other structures—like trees, rocks, or even the forest floor—to grow upward and outward.
These vines are often found in tropical and temperate forests, where they use their climbing ability to reach sunlight in dense canopies.
Types of Large Vines Found in Forests
Forests around the world host a wide variety of vines. Here are some of the most notable:
1. Tropical Forest Vines
- Lianas: These woody vines are iconic in rainforests. They twist and wrap around trees, creating dense networks.
- Rattan: Known for their strong, flexible stems, rattan vines are widely used in furniture and crafts.
- Monkey Ladder Vine: Found in the Amazon, this vine grows in unique, ladder-like patterns.
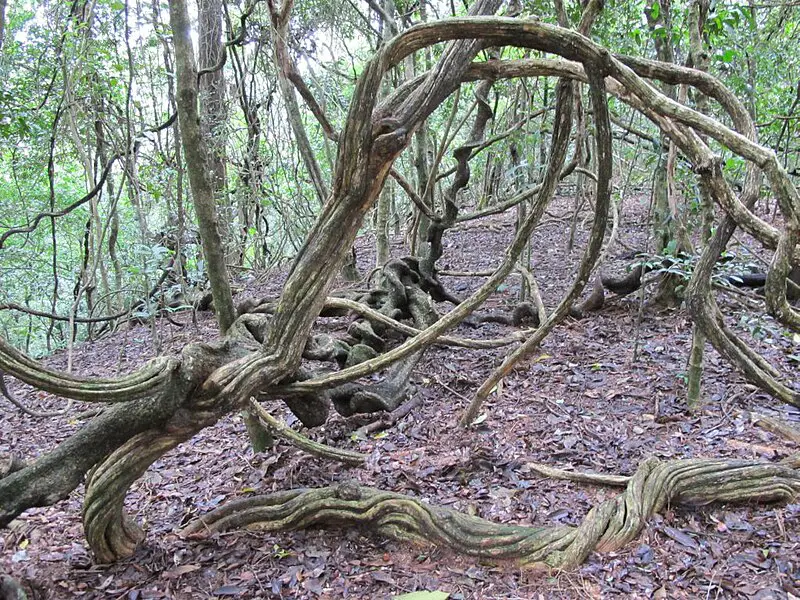

2. Temperate Forest Vines
- Wild Grape Vines: These vines produce small fruits and are common in North American forests.
- Virginia Creeper: A fast-growing climber with vibrant red leaves in autumn.
- Poison Ivy: Although harmful to humans, it’s an important food source for wildlife.
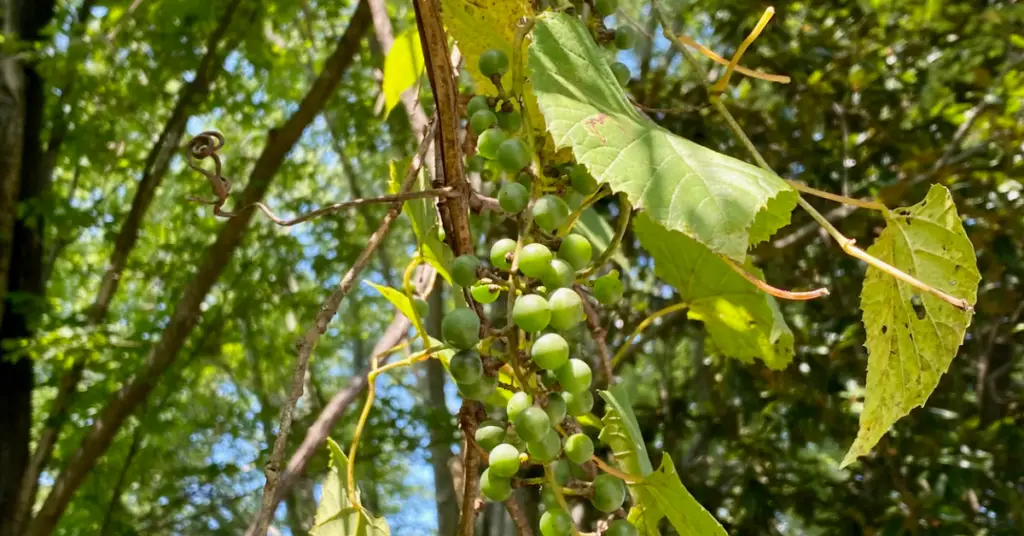

3. Invasive Vines
- Kudzu: Nicknamed “the vine that ate the South,” Kudzu spreads quickly and smothers native plants.
- English Ivy: While decorative, it can overwhelm forest floors and trees.
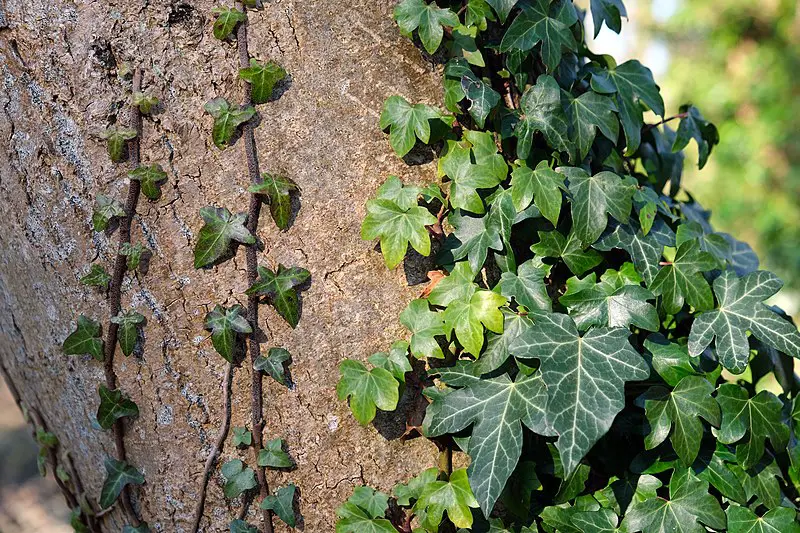

Why Are Large Vines Important?
1. Supporting Wildlife
Vines provide food, shelter, and pathways for forest creatures. Birds, insects, and mammals use vines for nesting and foraging.
2. Stabilizing Soil
By growing along the ground or wrapping around trees, vines prevent soil erosion, especially in sloped areas.
3. Enhancing Forest Canopies
Vines connect trees and fill gaps in the canopy, which helps maintain the forest’s microclimate.
4. Human Uses
Many vines, like rattan and certain lianas, are harvested for their flexible and durable stems. These materials are used to make furniture, ropes, and traditional tools.
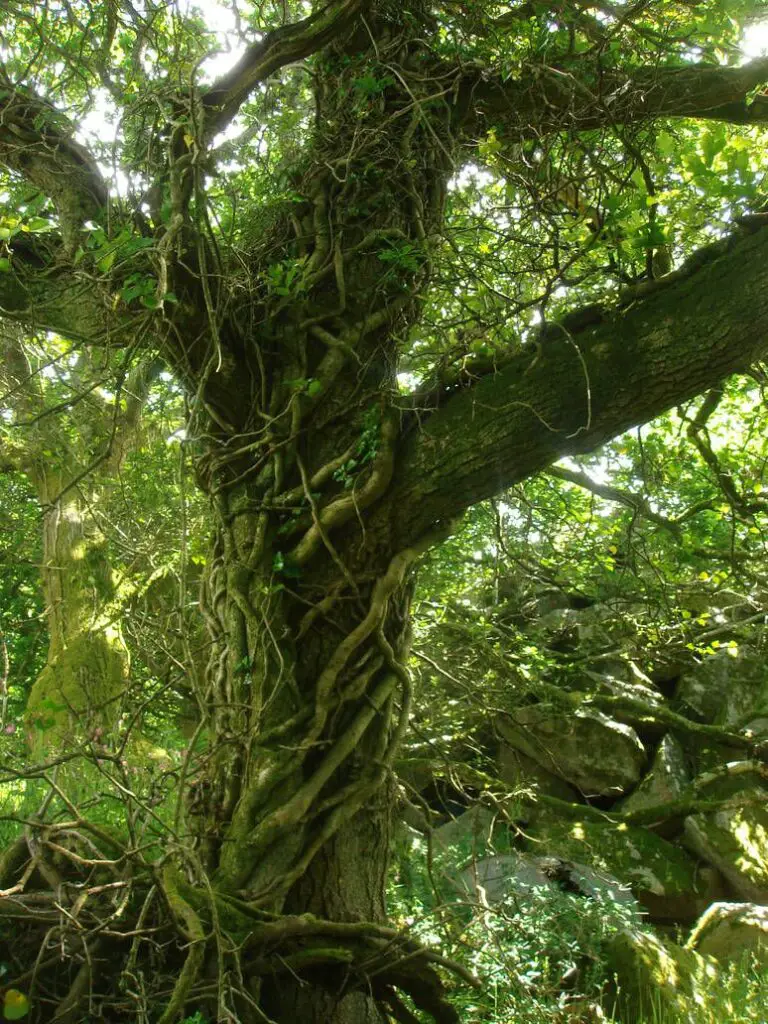

Challenges Posed by Large Vines
1. Competition with Trees
Some vines grow so aggressively that they overtake trees, blocking sunlight and stunting growth.
2. Invasive Species
Non-native vines like Kudzu can outcompete local plants, disrupting ecosystems.
3. Impact on Biodiversity
Overgrowth can lead to a monoculture of vines, reducing the diversity of plants and animals in the forest.
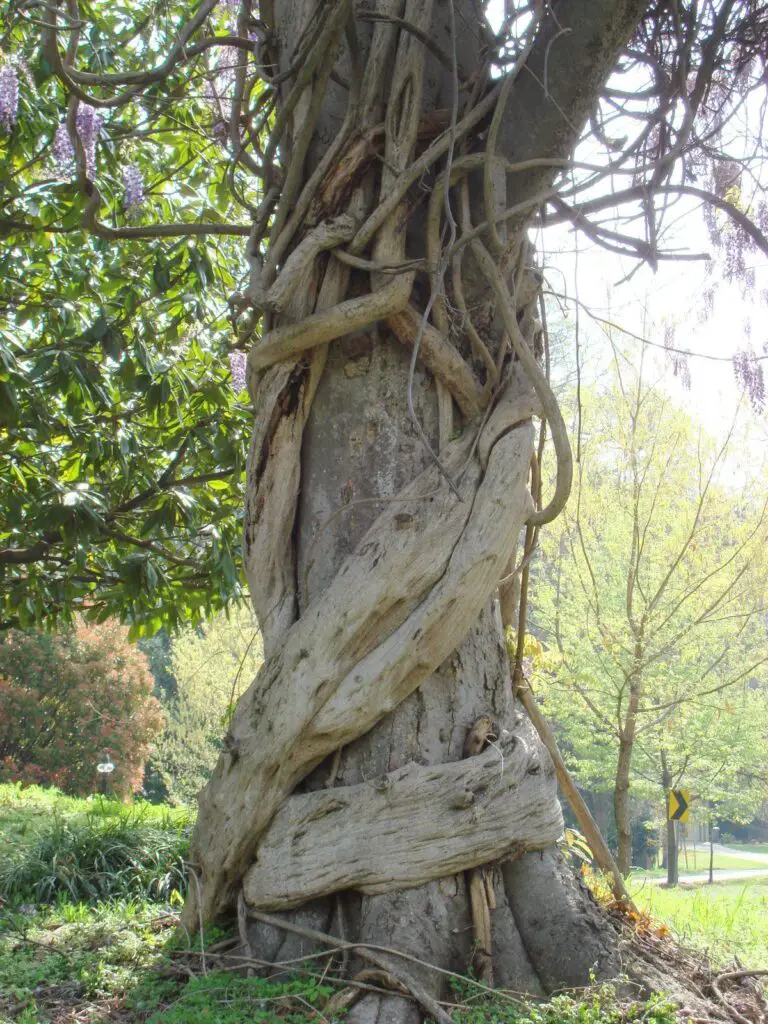

How Do Large Vines Grow?
1. Climbing Mechanisms
Vines climb in several ways:
- Twining: Wrapping around a support (e.g., Lianas).
- Tendrils: Using small, coiling structures to grip.
- Adhesive Pads: Sticking to surfaces (e.g., Virginia Creeper).
2. Environmental Factors
Vines thrive in moist, nutrient-rich soils and areas with strong sunlight. However, their growth can be affected by drought, deforestation, and changes in climate.
Iconic Forests Known for Large Vines
- Amazon Rainforest: Home to thousands of vine species, including lianas.
- Congo Rainforest: Features massive networks of climbing plants.
- Southeast Asian Forests: Known for rattan vines and dense jungle vegetation.
Conservation and Management of Forest Vines
Balancing the benefits and challenges of vines is essential for healthy ecosystems. Conservation efforts focus on:
- Promoting native species.
- Controlling invasive vines through manual removal or herbicides.
- Educating communities about sustainable harvesting practices.
FAQs
1. Can large vines harm trees?
Yes, some aggressive vines can block sunlight and add weight, which may weaken or kill trees over time.
2. Are all forest vines safe to touch?
No. Vines like poison ivy can cause skin irritation. Always identify vines before touching them.
3. How can you identify common forest vines?
Look for unique traits like leaves, climbing mechanisms, and fruits. Field guides and apps can help too.
Conclusion
Large vines are more than just plants; they’re vital parts of forest ecosystems. From supporting wildlife to connecting the canopy, they play countless roles in keeping forests healthy and vibrant. However, like all parts of nature, they require balance. By understanding these climbing giants, we can appreciate their beauty and ensure they thrive without harming the ecosystems they call home.
Forests
Why Do People Need to Protect the Forests?

Key Takeaways
- Forests play a crucial role in maintaining the planet’s health by regulating the climate, providing oxygen, and supporting biodiversity.
- They are essential for human survival, offering food, medicine, shelter, and clean water.
- Threats like deforestation, climate change, and illegal activities make forest conservation an urgent necessity.
- Protecting forests requires global efforts, community participation, and individual action.
The Importance of Protecting Forests
Imagine a world without trees. The air we breathe would be polluted, countless animals would lose their homes, and natural disasters like floods would worsen. Forests are not just a collection of trees; they are life-support systems for the planet and everyone on it. So, why is it so important to protect them? Let’s dive into the details.
The Ecological Importance of Forests
Forests are the backbone of Earth’s ecosystems. They act as:
1. Biodiversity Hotspots
Forests are home to 80% of the world’s terrestrial plants, animals, and fungi. This means they’re essential for keeping life on Earth diverse and balanced. Without them, we’d lose species that are crucial for pollination, pest control, and maintaining food chains.

2. Natural Climate Regulators
Trees absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen. They’re like Earth’s lungs, keeping the atmosphere breathable. By storing carbon, forests help fight climate change. Without them, greenhouse gases would build up faster, leading to more extreme weather.
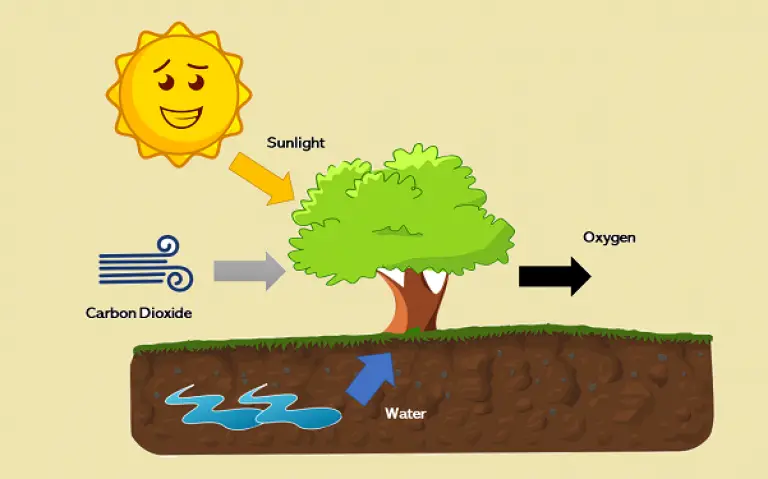
3. Protectors of Soil and Water
Tree roots hold soil in place, preventing erosion and landslides. Forests also regulate water cycles, ensuring clean water flows into rivers and reservoirs. Without forests, soil fertility drops, and water supplies shrink.

Forests and Human Well-Being
Forests don’t just benefit the environment—they’re essential for human life too.
1. Source of Oxygen and Clean Air
One large tree can supply a day’s worth of oxygen for four people. Trees also filter out air pollutants, making cities and rural areas healthier to live in.

2. Providers of Resources
Forests provide wood, fruits, nuts, and medicinal plants. Many life-saving drugs, like cancer treatments, come from forest plants. Forests also supply raw materials for industries, supporting millions of jobs worldwide.

3. Livelihoods for Communities
Millions of people, especially Indigenous communities, depend on forests for food, shelter, and cultural traditions. For them, forests are not just resources—they’re life itself.

4. Natural Therapy
Walking in a forest can reduce stress, lower blood pressure, and boost mental health. Forests offer a peaceful escape from busy, modern life.

The Threats Forests Face
Sadly, forests are under constant threat, and the damage is accelerating.
1. Deforestation
Forests are being cut down for agriculture, urban development, and logging. Every year, about 10 million hectares of forest are lost—equivalent to 27 football fields every minute.

2. Climate Change
Rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns are making forests drier and more vulnerable to wildfires. These fires destroy habitats and release massive amounts of carbon dioxide.
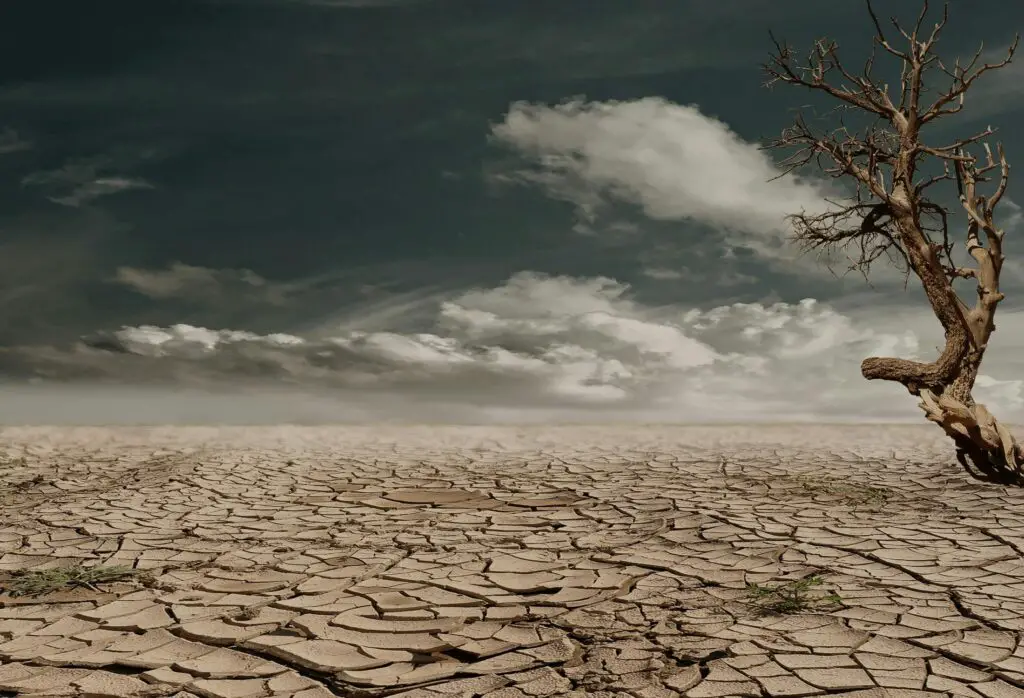

3. Illegal Activities
Illegal logging, mining, and poaching are devastating forests worldwide. These actions not only harm ecosystems but also deprive local communities of their livelihoods.
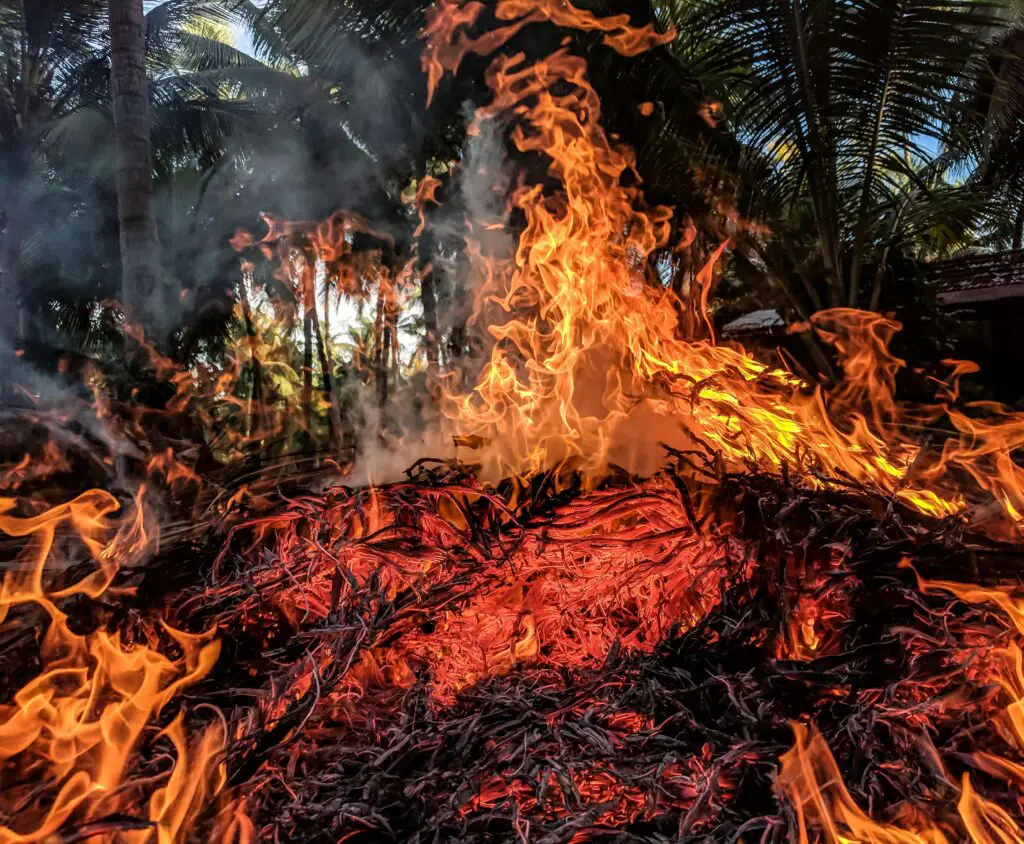

4. Pollution
Toxins from industries and agriculture seep into forest soils and water systems, damaging plants and wildlife.
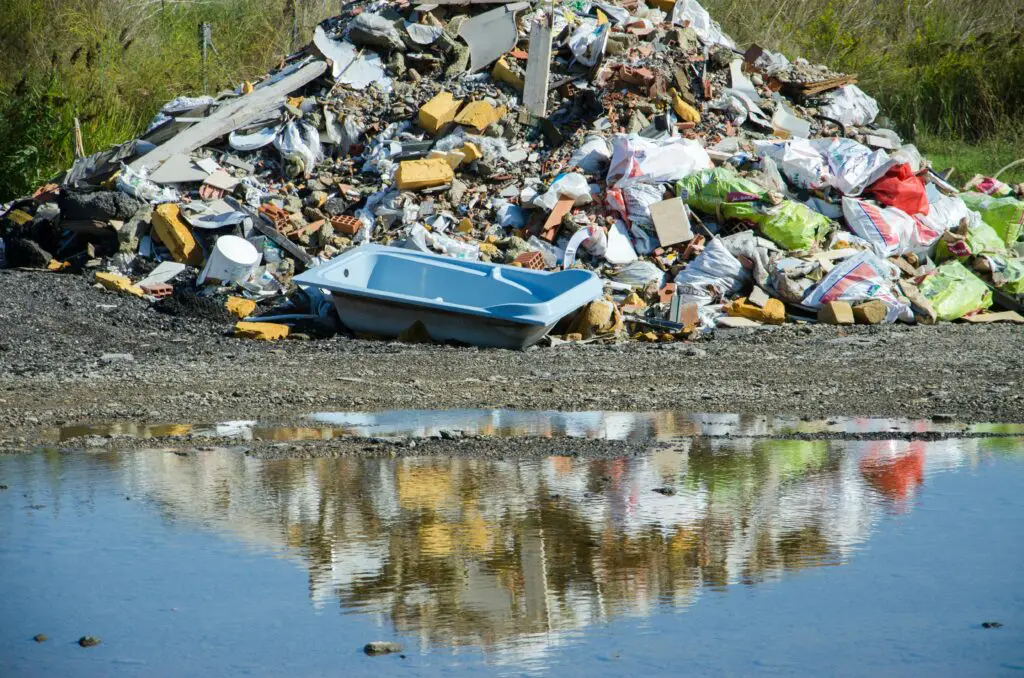

Why Protecting Forests Is Essential
Forests are irreplaceable. Here’s why saving them matters:
- Combat Climate Change: Forests absorb nearly a third of the carbon dioxide emitted by human activities. Losing them accelerates global warming.
- Preserve Biodiversity: Forests are home to countless species that are vital for ecological balance.
- Secure Water Supplies: Forests protect watersheds that supply drinking water to billions of people.
- Reduce Natural Disasters: Forests act as barriers against floods, landslides, and storms.
How Can We Protect Forests?
Saving forests requires action at all levels. Here’s how we can help:
1. Reforestation and Afforestation
Planting trees is one of the best ways to restore damaged forests. Governments and communities worldwide are launching tree-planting initiatives to combat deforestation.
2. Sustainable Practices
Switch to sustainable farming, logging, and mining methods to reduce environmental damage. For example, agroforestry combines agriculture and tree planting to maintain soil fertility.
3. Stronger Laws and Policies
Governments must enforce laws to protect forests from illegal logging and mining. Supporting international agreements like the Paris Agreement is crucial too.
4. Community Involvement
Local communities often know the best ways to manage forests sustainably. Supporting their efforts through education and funding is key.
5. Individual Actions
- Reduce paper and wood waste.
- Support brands that use eco-friendly materials.
- Donate to organizations working to protect forests, like WWF or Rainforest Alliance.
- Educate others about the importance of forests.
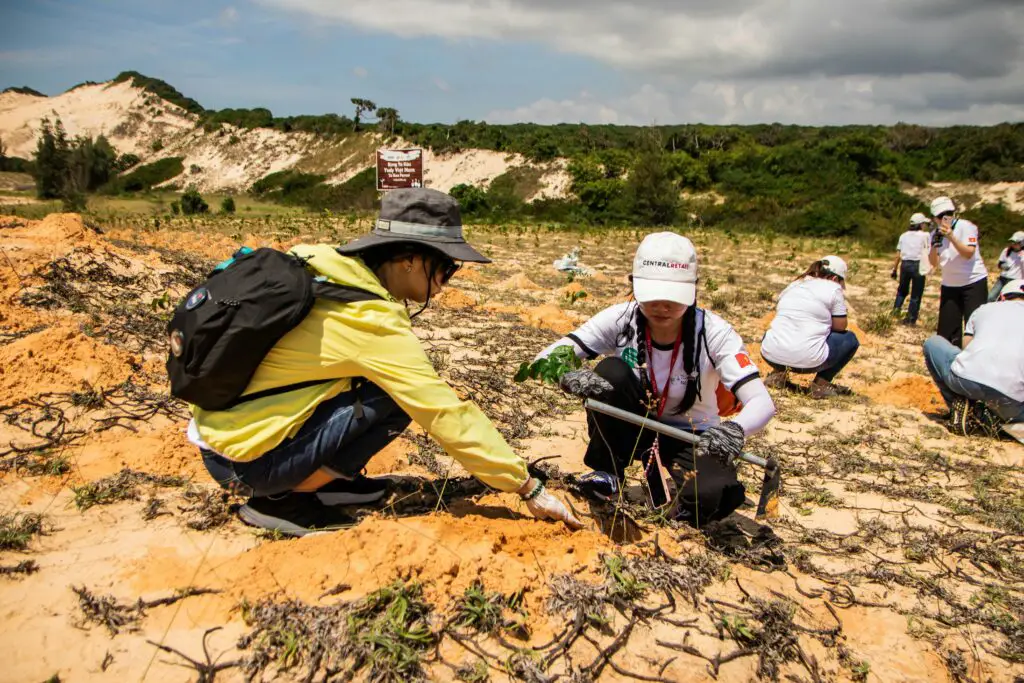

Success Stories in Forest Conservation
Efforts to protect forests are making a difference:
- In Costa Rica, reforestation projects have doubled forest cover over the last 30 years.
- The Amazon Fund is helping to combat deforestation in the world’s largest rainforest.
- India’s Chipko Movement, where villagers hugged trees to prevent logging, inspired global environmental movements.
FAQs
Why are forests called Earth’s lungs?
Forests absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen during photosynthesis, just like lungs help us breathe.
What happens if we lose forests?
Losing forests leads to more greenhouse gases, less biodiversity, water scarcity, and increased natural disasters.
Can reforestation reverse climate change?
While reforestation helps, it’s not a complete solution. We must also reduce carbon emissions and protect existing forests.
Conclusion
Forests are more than just trees—they’re life itself. Protecting them is not just an environmental issue; it’s a matter of survival. Whether it’s planting trees, supporting sustainable products, or spreading awareness, every action counts. Let’s work together to protect the forests, for our planet and future generations.
-

 Animals1 year ago
Animals1 year agoTypes of Ants Living in the World and Information
-

 Forests1 year ago
Forests1 year agoThe 10 Best Forests to Visit in the World
-

 Ocean1 year ago
Ocean1 year agoOceans in the World and Their Information & Locations
-

 Forests4 years ago
Forests4 years agoWhat Is The Biggest Rainforest In The World?
-

 Animals4 years ago
Animals4 years agoMost Popular Wild Animals in The World
-

 Animals4 years ago
Animals4 years ago(10) Insects Are Animals in the world?
-

 Nature1 year ago
Nature1 year agoThe 10 Largest Farms in the World
-

 Plants and Trees4 years ago
Plants and Trees4 years agoBiggest Trees in The World List




