Animals
Types of Ants Living in the World and Information
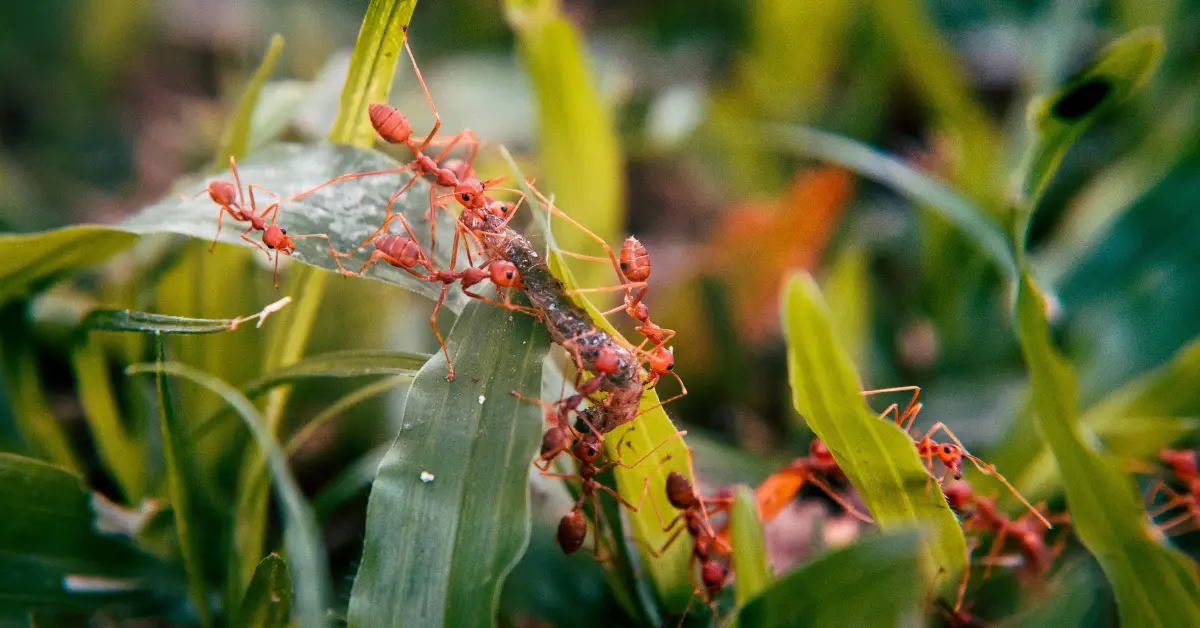

Key Takeaways
- There are over 12,000 species of ants identified worldwide, with diverse habitats and behaviors.
- Some common types include carpenter ants, fire ants, sugar ants, and leafcutter ants.
- Ants play vital roles in ecosystems but can also be invasive pests in certain contexts.
- Understanding different types of ants helps in appreciating their ecological importance and managing their presence effectively.
Ants: Nature’s Tiny Yet Mighty Creatures
Ants might be small, but their impact on the environment is enormous. Found almost everywhere on Earth, these fascinating insects have over 12,000 species that vary in size, behavior, and habitat. From their intricate colonies to their ability to adapt and thrive in diverse conditions, ants are nothing short of amazing.
If you’ve ever wondered about the types of ants crawling around the world and their unique characteristics, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive deep into the world of ants and uncover the details you’ve been curious about.
How Many Types of Ants Exist Worldwide?
Ants belong to the family Formicidae, and researchers have identified more than 12,000 species globally, with many more yet to be discovered. They are grouped into various genera and species based on their physical traits, behaviors, and habitats.
Tropical regions, like the Amazon rainforest, are home to the highest diversity of ants. However, you can find them in deserts, forests, urban areas, and even your backyard!
Common Types of Ants and Their Characteristics
Here are some of the most common types of ants found worldwide:
1. Carpenter Ants
- Where They Live: Forests, wooden structures, and dead trees.
- Why They’re Special: These ants are famous for their ability to burrow into wood, which can sometimes cause damage to homes. They don’t eat wood but use it to create their nests.
- Geographic Range: Found across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia.

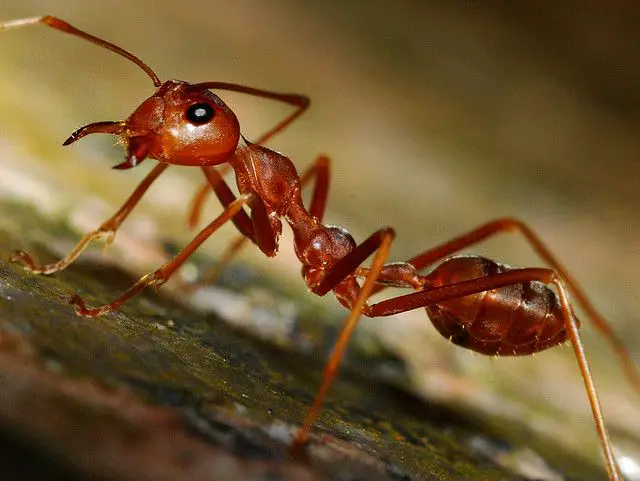
2. Fire Ants
- Where They Live: Warm climates, particularly in South America and the southern United States.
- Why They’re Special: Known for their painful sting, fire ants are aggressive and can pose a threat to humans and animals.
- Behavior: They form large colonies and are highly territorial.

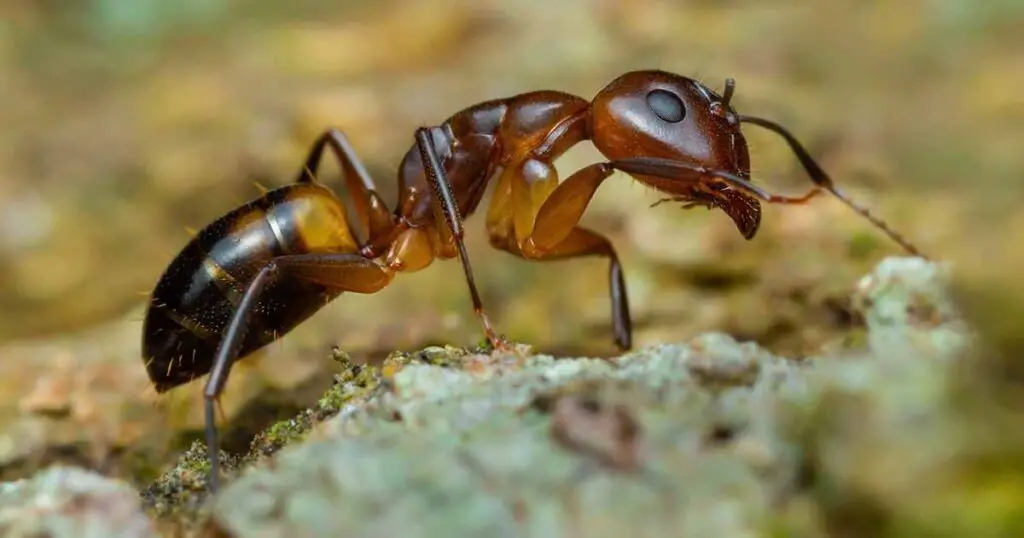
3. Sugar Ants
- Where They Live: Near human settlements where sugary food is available.
- Why They’re Special: Attracted to sweet foods, sugar ants are common household pests.
- Behavior: Mostly harmless but annoying due to their foraging habits.

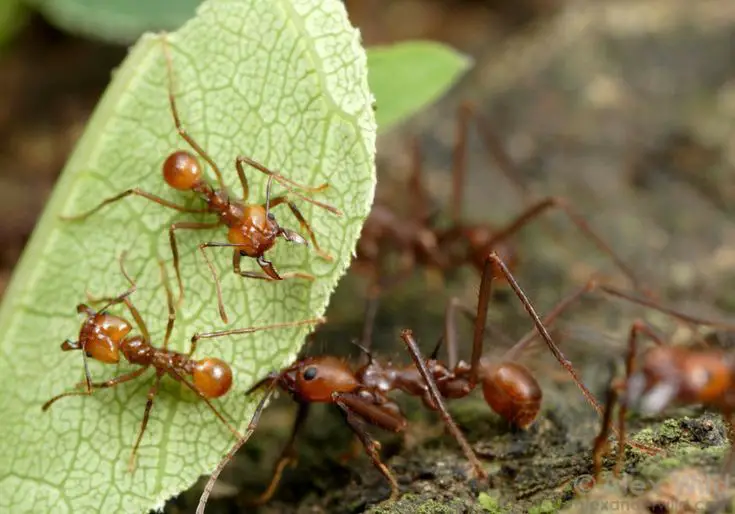
4. Leafcutter Ants
- Where They Live: Tropical rainforests in South and Central America.
- Why They’re Special: These ants are nature’s farmers, cutting leaves to cultivate fungus, which serves as their primary food source.
- Ecological Role: Essential for nutrient cycling in forests.
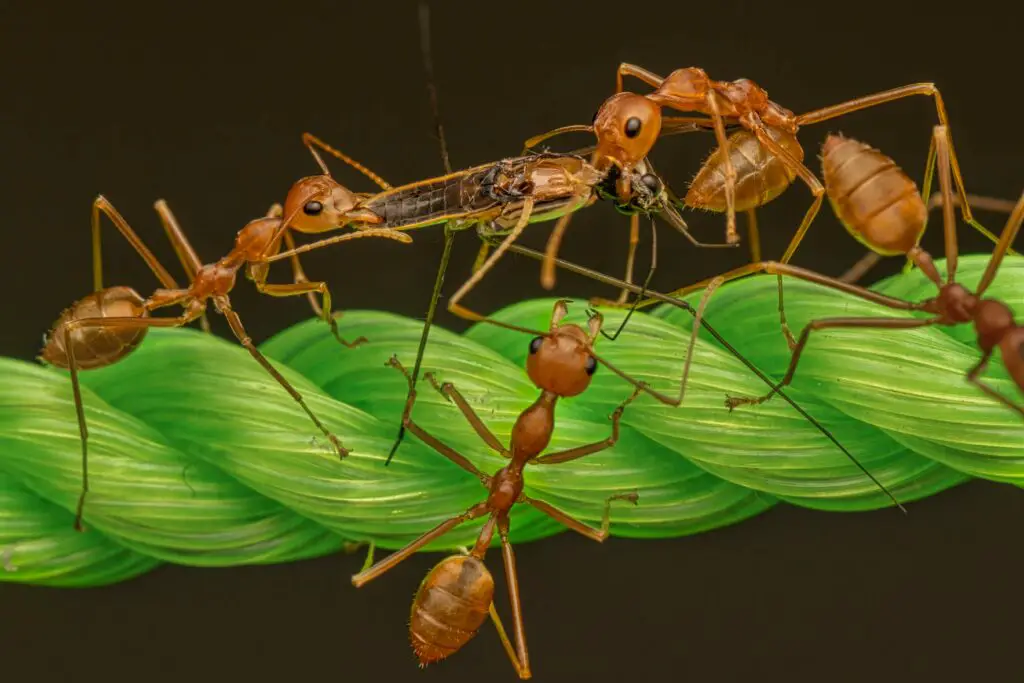

5. Army Ants
- Where They Live: Tropical regions, especially in Africa and South America.
- Why They’re Special: Known for their nomadic lifestyle and coordinated hunting strategies.
- Behavior: Travel in massive swarms to hunt prey.

Where Ants Live and Thrive
Ants are incredibly adaptable and can live in almost any environment. Here are some key habitats:
- Tropical Regions: Rich biodiversity and food availability make these areas ideal.
- Urban Areas: Many ants thrive in human settlements due to easy access to food and shelter.
- Deserts: Species like the harvester ant have adapted to extreme heat and arid conditions.
Unique Behaviors and Social Structure
Ants have complex social structures that make their colonies highly efficient. Each colony has a queen, workers, and sometimes soldiers. Their communication relies on pheromones, sounds, and touch, enabling them to work together seamlessly.
Interesting behaviors include:
- Farming: Leafcutter ants grow fungus as food.
- Swarming: Army ants hunt in groups to capture larger prey.
- Nest Building: Carpenter ants carve intricate tunnels in wood.
Benefits and Challenges of Ants
Ants are essential for ecosystems:
- Benefits:
- Aerate soil and help plants grow.
- Control pests by eating other insects.
- Recycle organic material.
- Challenges:
- Some species, like fire ants, are invasive and harmful.
- Carpenter ants can damage wooden structures.
FAQs About Ants
1. Why are ants important in ecosystems?
Ants help aerate the soil, control pests, and recycle organic material, making them vital for the environment.
2. How can I identify different ant species?
Look at their size, color, behavior, and where they live. Using a guidebook or online resources can also help.
3. Are all ants harmful?
No, most ants are harmless. Some can be pests, but others play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance.
Conclusion
Ants may be small, but they’re incredibly diverse and vital to the natural world. From carpenter ants burrowing in wood to leafcutter ants farming fungus, each species has a unique story to tell. By understanding more about these fascinating creatures, we can appreciate their roles in the ecosystem and learn to coexist with them.
Image Article Source : https://www.pinterest.com/
Animals
20 Most Poisonous Snakes in the World

Hey, nature lovers! Ever wondered what makes some snakes so deadly that just one bite can change everything? If you’re out hiking or just love learning about wildlife, knowing about these poisonous creatures can keep you safe and amazed. We’ve put together a list of the 20 most poisonous snakes out there, based on how strong their venom is. Stick around – you might be surprised by what’s lurking in the wild!
Key Takeaways
- These snakes have super strong venom that can harm people fast.
- Most live in places like Australia, Asia, and Africa, but some are closer to home.
- Learning about them helps you stay safe outdoors.
- Venom potency is measured by things like LD50, which shows how little it takes to be deadly.
- Not all poisonous snakes are aggressive – many bite only when scared.
Summary Table of the 20 Most Poisonous Snakes
| Snake | Venom Type | Main Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Inland Taipan | Neurotoxic | Australia |
| 2. Eastern Brown Snake | Neurotoxic and Coagulant | Australia |
| 3. Coastal Taipan | Neurotoxic | Australia and New Guinea |
| 4. Tiger Snake | Neurotoxic and Myotoxic | Australia |
| 5. Black Mamba | Neurotoxic | Africa |
| 6. Philippine Cobra | Neurotoxic | Philippines |
| 7. Death Adder | Neurotoxic | Australia and New Guinea |
| 8. Belcher’s Sea Snake | Neurotoxic | Oceans near Australia and Asia |
| 9. Russell’s Viper | Hemotoxic | Asia |
| 10. Saw-Scaled Viper | Hemotoxic | Middle East and India |
| 11. King Cobra | Neurotoxic | Asia |
| 12. Boomslang | Hemotoxic | Africa |
| 13. Fer-de-Lance | Hemotoxic | Central and South America |
| 14. Bushmaster | Hemotoxic | South America |
| 15. Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake | Hemotoxic | USA |
| 16. Coral Snake | Neurotoxic | Americas |
| 17. Common Krait | Neurotoxic | Asia |
| 18. Blue Krait | Neurotoxic | Southeast Asia |
| 19. Many-Banded Krait | Neurotoxic | Asia |
| 20. Beaked Sea Snake | Neurotoxic | Oceans in Indo-Pacific |
This table gives you a quick look. Now, let’s dive deeper into each one. You’re going to love the details – it’s like uncovering secrets of nature!
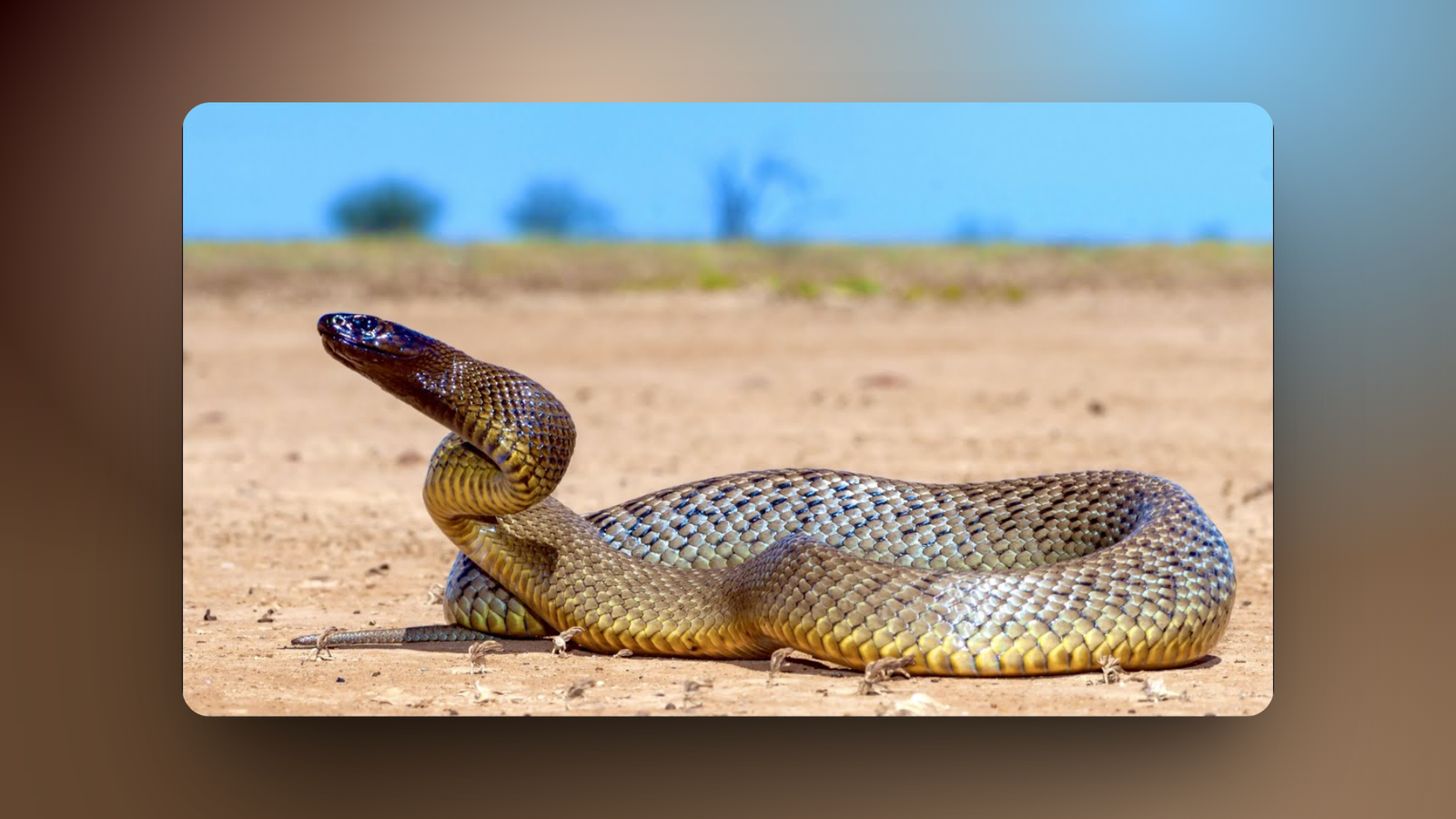
1. Inland Taipan
About
The Inland Taipan, also called the fierce snake, is from the Elapidae family. Its scientific name is Oxyuranus microlepidotus. It was first described in 1879, but people didn’t know much about it until the 1970s because it’s so shy and lives in remote areas. This snake is native to central Australia and is known as the most venomous land snake in the world.
Description
This snake grows up to about 2 meters long, that’s around 6.5 feet. It has a slim body with scales that look smooth and can be light brown or olive green, which helps it blend into the dry grasslands. Its head is a bit wider than the neck, and it has big eyes with round pupils. When it’s angry, it can flatten its neck a little, but not like a cobra. The color changes with seasons – darker in winter to soak up more heat.
Venom
The venom is mostly neurotoxic, which means it attacks the nerves and can stop you from breathing. One bite has enough venom to kill 100 people! The LD50 value is super low at 0.025 mg/kg, making it the strongest. It also has some myotoxins that damage muscles. If bitten, symptoms start fast: headache, nausea, then paralysis. Without treatment, it’s deadly in under an hour.
Habitat
You’ll find the Inland Taipan in the dry, cracked soil areas of Queensland and South Australia. It likes hiding in rat burrows or under rocks during the hot days. These snakes are active in the morning or late afternoon to avoid the extreme heat. They eat mostly small mammals like rats, which they hunt in the semi-arid plains.
Why It’s Dangerous
This snake is dangerous because its venom is so potent – even a tiny amount can cause total body shutdown. But here’s the good news: it’s not aggressive and bites only if cornered. Most bites happen to snake handlers. If you’re in its area, watch your step, and antivenom works well if you get help quick. Knowing this keeps you on the edge of your seat when exploring Aussie outback!
Key Facts
- Average length: 1.8-2.5 meters.
- Diet: Small rodents.
- Lifespan: Up to 20 years in captivity.
- Conservation status: Least concern, but habitat loss is a worry.
For more on deadly animals, check our article on Most Dangerous Animals in Australia. Learn more from National Geographic.
2. Eastern Brown Snake
About
The Eastern Brown Snake is part of the Elapidae family, scientific name Pseudonaja textilis. It was named in 1801 and is common in eastern Australia. This snake is responsible for many snakebite deaths there because it lives near people.
Description
It can reach up to 2 meters, with a slender build and colors from light tan to dark brown. The belly is cream or yellow. Young ones have black bands on their heads, which fade as they grow. It’s fast and can raise its body when threatened, looking ready to strike.
Venom
Neurotoxic and coagulant venom makes blood clot wrong and attacks nerves. LD50 is 0.036 mg/kg. Bites cause pain, swelling, then bleeding issues and paralysis. Untreated, it can kill in hours.
Habitat
Lives in farmlands, woodlands, and even suburbs in eastern Australia. It hides under logs or in grass and hunts during the day.
Why It’s Dangerous
It’s quick to bite if surprised, and since it likes areas with humans, encounters happen a lot. But antivenom saves most people. Stay alert in grassy spots!
Key Facts
- Length: 1.5-2 meters.
- Diet: Rodents, birds, frogs.
- Lifespan: 7-10 years.
- It’s the second most venomous land snake.
See related: Deadliest Snakes in Asia.
3. Coastal Taipan
About
From the Elapidae family, Oxyuranus scutellatus, described in 1867. Native to northern Australia and New Guinea.
Description
Up to 3 meters long, brown or black with a lighter head. Slim and agile.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.099 mg/kg. Causes rapid paralysis and bleeding.
Habitat
Coastal forests and cane fields, active daytime hunter.
Why It’s Dangerous
Aggressive when cornered, venom acts fast. Rare bites, but deadly without help.
Key Facts
- Length: 2-3 meters.
- Diet: Mammals and birds.
- Known for multiple bites in one attack.
4. Tiger Snake
About
Notechis scutatus, Elapidae, named in 1827. Found in southern Australia.
Description
1-2 meters, with bands like a tiger, colors vary.
Venom
Neurotoxic and myotoxic, LD50 0.118 mg/kg. Damages muscles and nerves.
Habitat
Wetlands, rivers, active in cooler weather.
Why It’s Dangerous
Defensive, bites cause severe pain and organ failure.
Key Facts
- Adapts to cold by hibernating.
- Eats frogs and small animals.
5. Black Mamba
About
Dendroaspis polylepis, Elapidae, 1864. Africa’s longest venomous snake.
Description
Up to 4.5 meters, gray to olive, black mouth inside.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.25 mg/kg. Fast-acting, causes collapse in minutes.
Habitat
Savannas, rocky hills in sub-Saharan Africa.
Why It’s Dangerous
Very fast, up to 20 km/h, and territorial.
Key Facts
- Not actually black, name from mouth.
- Diet: Birds, mammals.
Link: African Wildlife Dangers. More at BBC Wildlife.
6. Philippine Cobra
About
Naja philippinensis, Elapidae, 1922. Endemic to the Philippines.
Description
1-1.5 meters, brown with hood.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.2 mg/kg. Spits venom too.
Habitat
Forests, fields, near water.
Why It’s Dangerous
Spits accurately, causes blindness or death.
Key Facts
- Can spit up to 3 meters.
- Eats small vertebrates.
7. Death Adder
About
Acanthophis antarcticus, Elapidae, 1804. Australia and New Guinea.
Description
Short, up to 1 meter, triangular head, banded.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.4 mg/kg. Paralyzes quickly.
Habitat
Forests, grasslands, ambush hunter.
Why It’s Dangerous
Camouflages well, strikes fast.
Key Facts
- Waits for prey, tail lures.
- Gives live birth.
8. Belcher’s Sea Snake
About
Hydrophis belcheri, Elapidae, 1849. Oceanic.
Description
Up to 1 meter, yellow with bands.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.24 mg/kg, but mild-mannered.
Habitat
Warm oceans, near reefs.
Why It’s Dangerous
Venom potent, but rare bites to fishermen.
Key Facts
- Most venomous sea snake.
- Eats fish.
9. Russell’s Viper
About
Daboia russelii, Viperidae, 1797. Asia.
Description
1-1.5 meters, brown with spots.
Venom
Hemotoxic, LD50 0.75 mg/kg. Causes bleeding, kidney failure.
Habitat
Grasslands, farms.
Why It’s Dangerous
Common in populated areas, aggressive.
Key Facts
- Hisses loudly.
- Major cause of bites in India.
10. Saw-Scaled Viper
About
Echis carinatus, Viperidae, 1799. Middle East, India.
Description
Small, 30-80 cm, rough scales.
Venom
Hemotoxic, LD50 0.24 mg/kg. Painful, causes hemorrhage.
Habitat
Deserts, rocky areas.
Why It’s Dangerous
Irritable, rubs scales to warn.
Key Facts
- Responsible for many deaths.
- Nocturnal.
11. King Cobra
About
Ophiophagus hannah, Elapidae, 1836. Asia.
Description
Up to 5.5 meters, olive with bands.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 1.28 mg/kg. Large quantity per bite.
Habitat
Forests, bamboo thickets.
Why It’s Dangerous
Eats other snakes, rears up high.
Key Facts
- Longest venomous snake.
- Builds nests for eggs.
12. Boomslang
About
Dispholidus typus, Colubridae, 1768. Africa.
Description
1.5-2 meters, green or brown, big eyes.
Venom
Hemotoxic, LD50 0.07 mg/kg. Slow but deadly bleeding.
Habitat
Trees, savannas.
Why It’s Dangerous
Rear-fanged, bites rare but fatal without antivenom.
Key Facts
- Changes color with age.
- Eats birds, chameleons.
13. Fer-de-Lance
About
Bothrops asper, Viperidae, 1766. Central/South America.
Description
Up to 2.5 meters, brown with diamonds.
Venom
Hemotoxic, LD50 1.1 mg/kg. Tissue damage, bleeding.
Habitat
Rainforests, plantations.
Why It’s Dangerous
Aggressive, common in human areas.
Key Facts
- Gives live birth.
- Nocturnal hunter.
14. Bushmaster
About
Lachesis muta, Viperidae, 1766. South America.
Description
Up to 3.5 meters, pinkish-brown with triangles.
Venom
Hemotoxic, LD50 1.5 mg/kg. Pain, swelling, death.
Habitat
Rainforests, solitary.
Why It’s Dangerous
Largest viper, strikes from distance.
Key Facts
- Vibrates tail like rattler.
- Eats small mammals.
15. Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake
About
Crotalus adamanteus, Viperidae, 1803. USA.
Description
Up to 2.5 meters, diamond pattern, rattle.
Venom
Hemotoxic, LD50 1.2 mg/kg. Damages tissue.
Habitat
Pine forests, swamps in Southeast US.
Why It’s Dangerous
Rattles to warn, but potent bite.
Key Facts
- Largest rattlesnake.
- Hunts rabbits, rodents.
Link: Snakes in North America.
16. Coral Snake
About
Micrurus fulvius, Elapidae, 1766. Americas.
Description
60-90 cm, red-yellow-black bands.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.3 mg/kg. Paralyzes slowly.
Habitat
Woodlands, under leaves.
Why It’s Dangerous
Mimicry confuses, small fangs but strong venom.
Key Facts
- Rhyme: “Red on yellow, kill a fellow.”
- Burrowing habits.
17. Common Krait
About
Bungarus caeruleus, Elapidae, 1799. Asia.
Description
1-1.5 meters, black with white bands.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.09 mg/kg. Bites at night, painless but deadly.
Habitat
Fields, villages.
Why It’s Dangerous
Enters homes, bites sleeping people.
Key Facts
- Nocturnal.
- Eats other snakes.
18. Blue Krait
About
Bungarus candidus, Elapidae, 1830. Southeast Asia.
Description
Up to 1.6 meters, black with blue tint, white bands.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.1 mg/kg. Causes paralysis.
Habitat
Forests, rice paddies.
Why It’s Dangerous
Quiet bites, high fatality without treatment.
Key Facts
- Similar to common krait.
- Active at night.
19. Many-Banded Krait
About
Bungarus multicinctus, Elapidae, 1861. Asia.
Description
1-1.5 meters, black with many white bands.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.08 mg/kg. Very potent.
Habitat
Mountains, forests.
Why It’s Dangerous
Bites cause respiratory failure fast.
Key Facts
- Found in Taiwan, China.
- Docile but deadly.
20. Beaked Sea Snake
About
Enhydrina schistosa, Elapidae, 1801. Indo-Pacific oceans.
Description
Up to 1.4 meters, gray with bands, paddle tail.
Venom
Neurotoxic, LD50 0.164 mg/kg. Affects nerves and muscles.
Habitat
Shallow seas, estuaries.
Why It’s Dangerous
Common in fishing nets, bites fishermen.
Key Facts
- Most dangerous sea snake for humans.
- Gives live birth in water.
FAQ
What’s the difference between poisonous and venomous snakes?
Venomous snakes inject venom through bites, while poisonous means harmful if eaten. All in this list are venomous – they bite to deliver toxin.
Which snake has the strongest venom?
The Inland Taipan tops the list with the most potent venom based on LD50 tests.
Are these snakes aggressive?
Most aren’t – they bite when threatened. Snakes like the Black Mamba can be territorial, though.
What should I do if bitten?
Stay calm, don’t move much, and get to a hospital fast for antivenom. Don’t suck out the venom!
Where can I see these snakes safely?
Visit zoos or wildlife sanctuaries. Never approach in the wild.
How can I avoid snake bites?
Wear boots in snake areas, watch your step, and don’t disturb rocks or logs.
Are sea snakes more dangerous than land ones?
Not always – their venom is strong, but they rarely bite unless handled.
Conclusion
There you have it – the 20 most poisonous snakes that make nature both thrilling and a bit scary. From the fierce Inland Taipan to the sneaky Beaked Sea Snake, each one shows how amazing wildlife can be. Learning about them isn’t just fun; it keeps you safe on your adventures. Don’t miss out on sharing this with fellow nature lovers – who knows, it might save a life! Share this post and tell us in the comments which snake surprised you most. For more, check Deadliest Creatures in the Ocean. Stay curious and safe out there!
Animals
The 10 Largest Living Birds in the World

Key Takeaways
- Discover the top 10 largest living birds by size and weight.
- Learn about their unique habitats, behaviors, and adaptations.
- Gain insight into how these birds survive and thrive in their environments.
Introduction
Birds are among the most fascinating creatures on Earth, and their incredible diversity never ceases to amaze us. From the small and colorful hummingbird to the towering ostrich, each species plays an important role in its ecosystem. But today, we’re going big—literally!
Have you ever wondered which birds hold the title of the largest living species in the world? This guide will take you on a journey to meet the giants of the bird kingdom. From massive flightless land birds to majestic fliers with astonishing wingspans, these species showcase just how remarkable nature can be.
Let’s dive into the top 10 largest living birds, exploring their size, habitats, and extraordinary traits that make them stand out.
The 10 Largest Living Birds
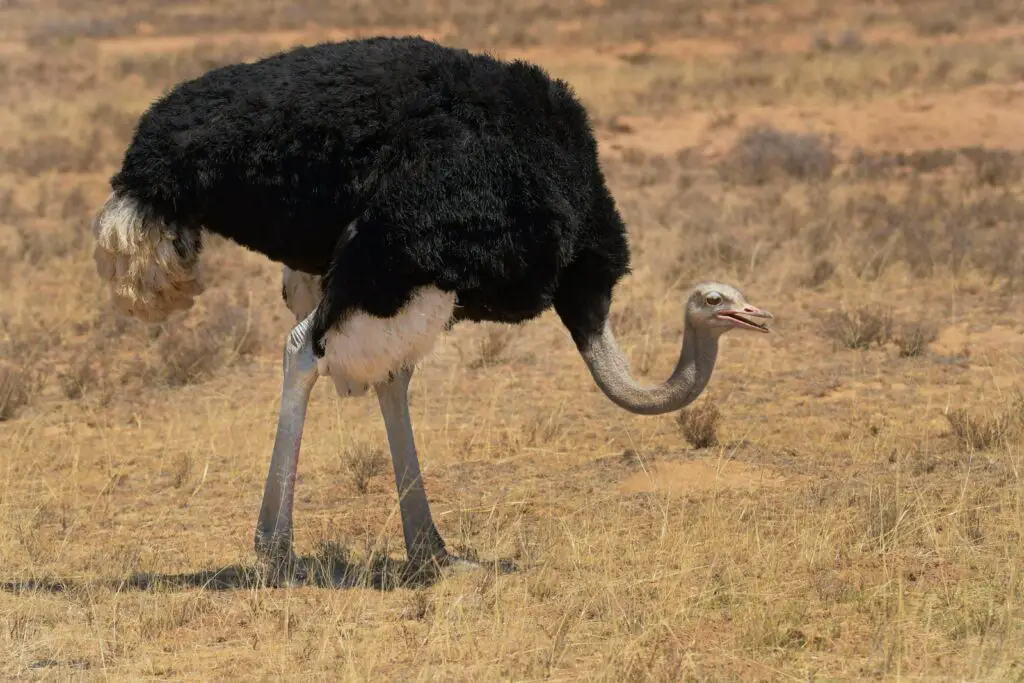
1. Ostrich – The Largest Living Bird
- Average Height: 8–9 feet
- Average Weight: 220–350 pounds
- Habitat: African savannas and deserts
The ostrich is not just the largest bird on the planet but also the fastest runner among birds, reaching speeds of up to 60 mph. They have powerful legs that allow them to cover up to 16 feet in a single stride. Being flightless, ostriches rely on their speed and size to evade predators.

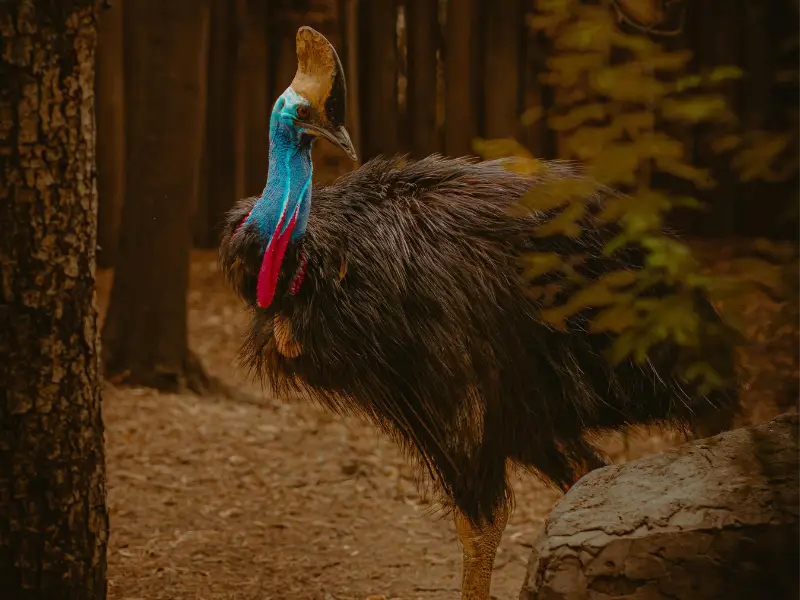
2. Southern Cassowary – The Forest Giant
- Average Height: 5–6.6 feet
- Average Weight: 110–160 pounds
- Habitat: Tropical forests of Australia, New Guinea, and nearby islands
Known for its striking blue neck and helmet-like casque, the southern cassowary is a solitary and territorial bird. While flightless, it’s an excellent swimmer and can navigate rivers with ease. Beware—this bird is known for its strong legs and sharp claws!

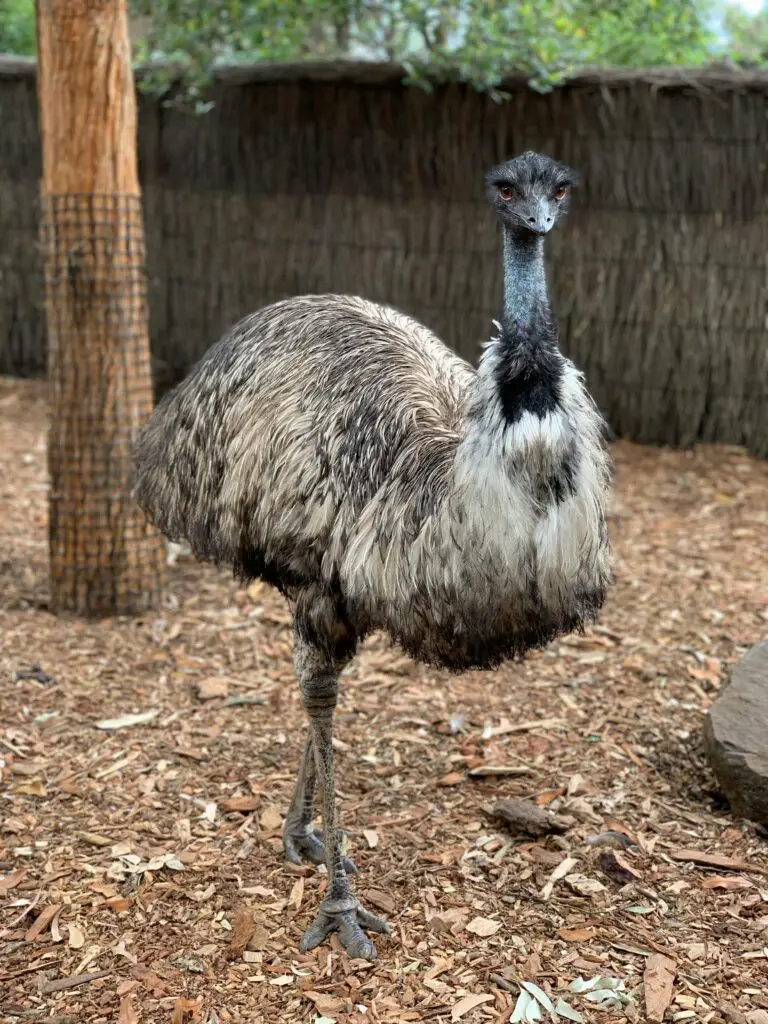
3. Emu – Australia’s Iconic Bird
- Average Height: 5.7–6.2 feet
- Average Weight: 100–130 pounds
- Habitat: Grasslands, woodlands, and semi-arid regions of Australia
The emu is a close cousin to the cassowary and shares its flightless nature. These curious birds are known for their inquisitive behavior and can travel long distances while searching for food.\

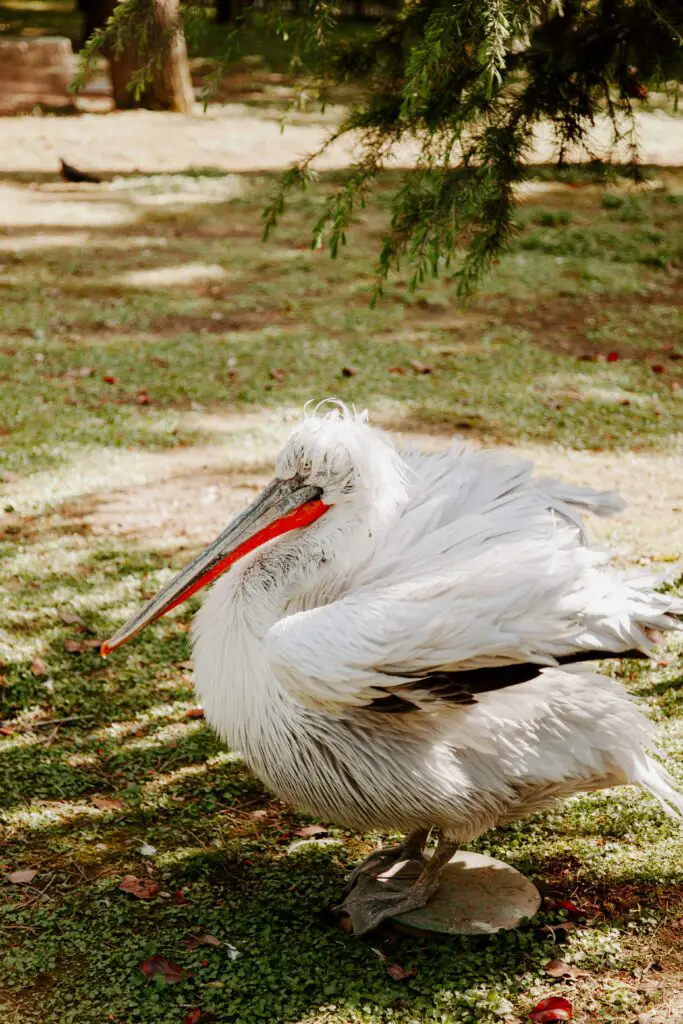
4. Dalmatian Pelican – The Largest Flying Bird by Weight
- Wingspan: 9–11.5 feet
- Average Weight: 22–33 pounds
- Habitat: Wetlands across Europe and Asia
This elegant bird is the heaviest flying bird in the world. Its enormous wingspan allows it to soar effortlessly, while its large pouch helps it catch fish. Dalmatian pelicans often live in colonies near lakes and rivers.

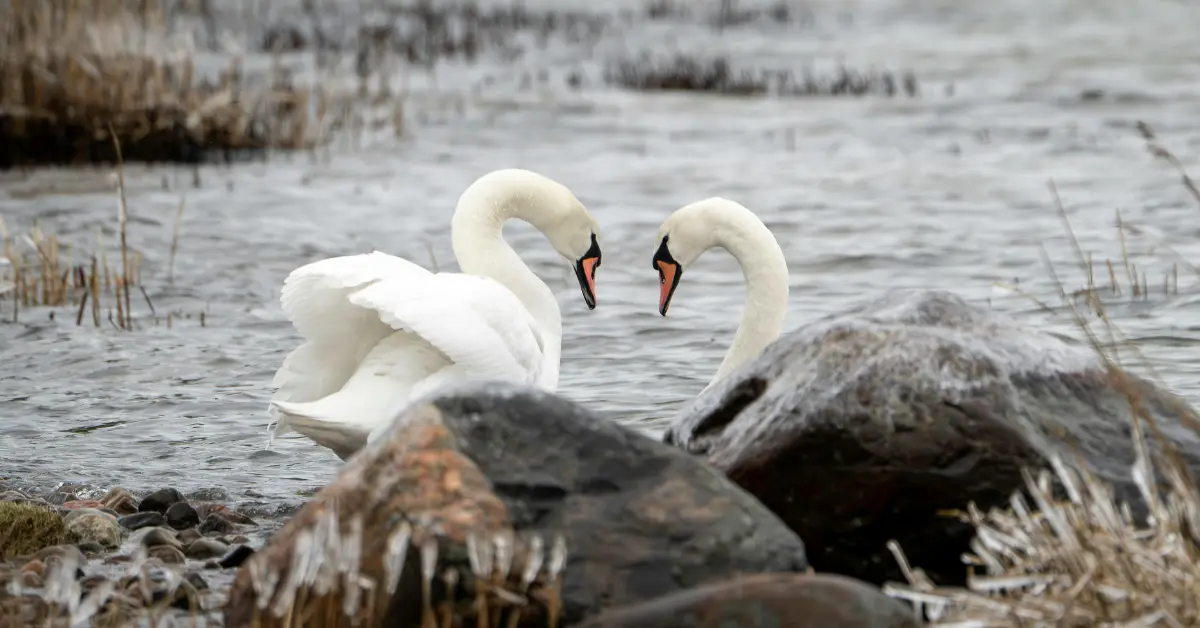
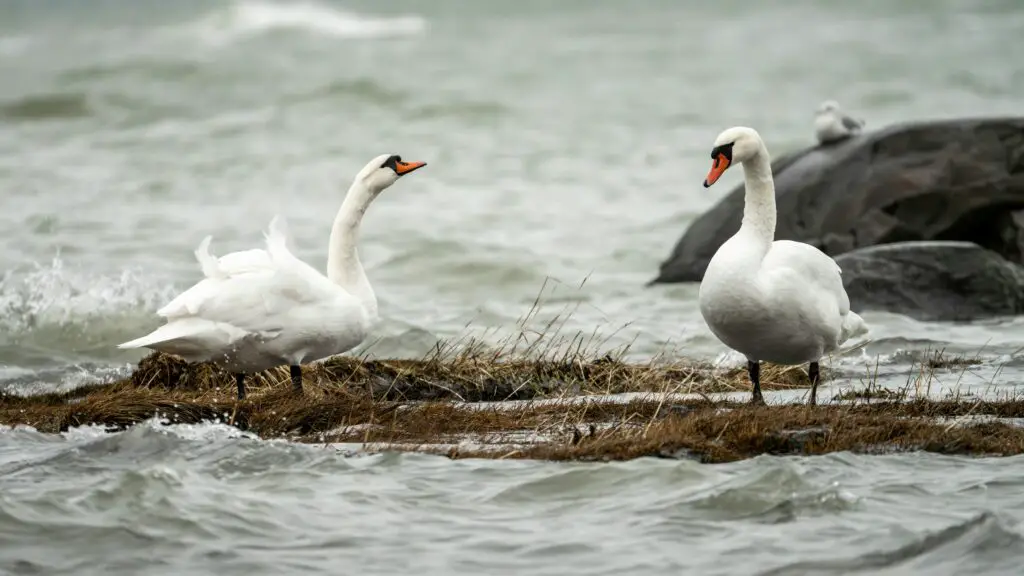
5. Mute Swan – Grace and Size Combined
- Wingspan: 7–8 feet
- Average Weight: 20–26 pounds
- Habitat: Lakes and ponds in Europe, Asia, and North America
Known for their elegant white feathers and curved necks, mute swans are among the largest waterfowl. Despite their serene appearance, they are highly territorial and can be aggressive when protecting their nests.

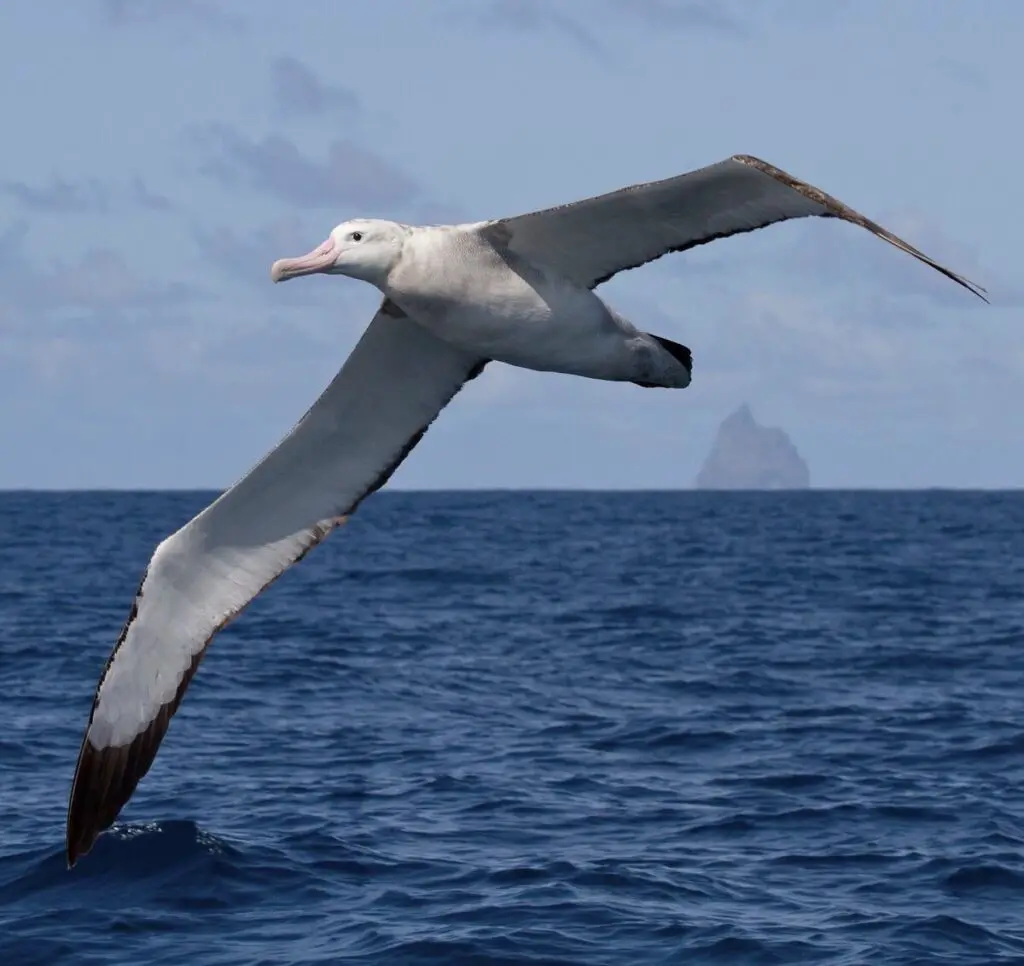
6. Wandering Albatross – The Bird with the Longest Wingspan
- Wingspan: 11–12 feet
- Average Weight: 15–25 pounds
- Habitat: Southern Ocean and sub-Antarctic islands
Famous for their incredible wingspan, wandering albatrosses can glide for hours without flapping their wings. They spend most of their lives at sea and are master navigators, traveling thousands of miles across the ocean.

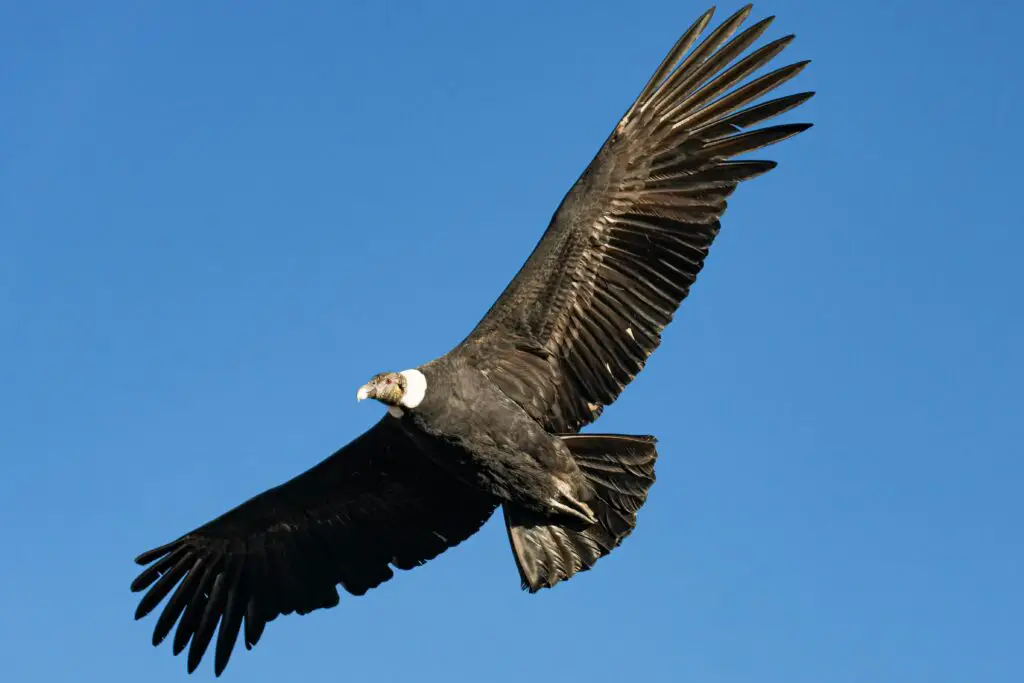
7. Andean Condor – The Largest Bird of Prey
- Wingspan: 9–10.5 feet
- Average Weight: 20–33 pounds
- Habitat: Andes Mountains of South America
This majestic scavenger is a symbol of the Andes. With its broad wings and impressive gliding ability, the Andean condor relies on thermals to soar high above the mountains in search of carrion.

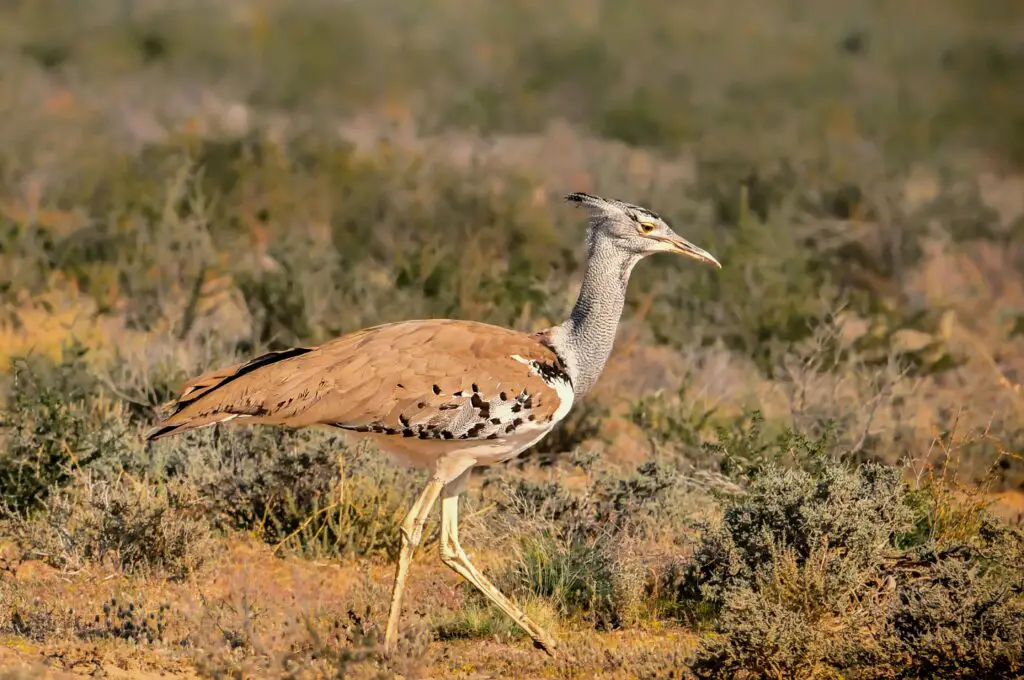
8. Kori Bustard – The Heaviest Flying Bird
- Average Weight: 24–42 pounds
- Habitat: African savannas and dry grasslands
The kori bustard holds the record for being the heaviest bird capable of flight. While they prefer walking and are not strong fliers, these birds display fascinating courtship dances during the breeding season.

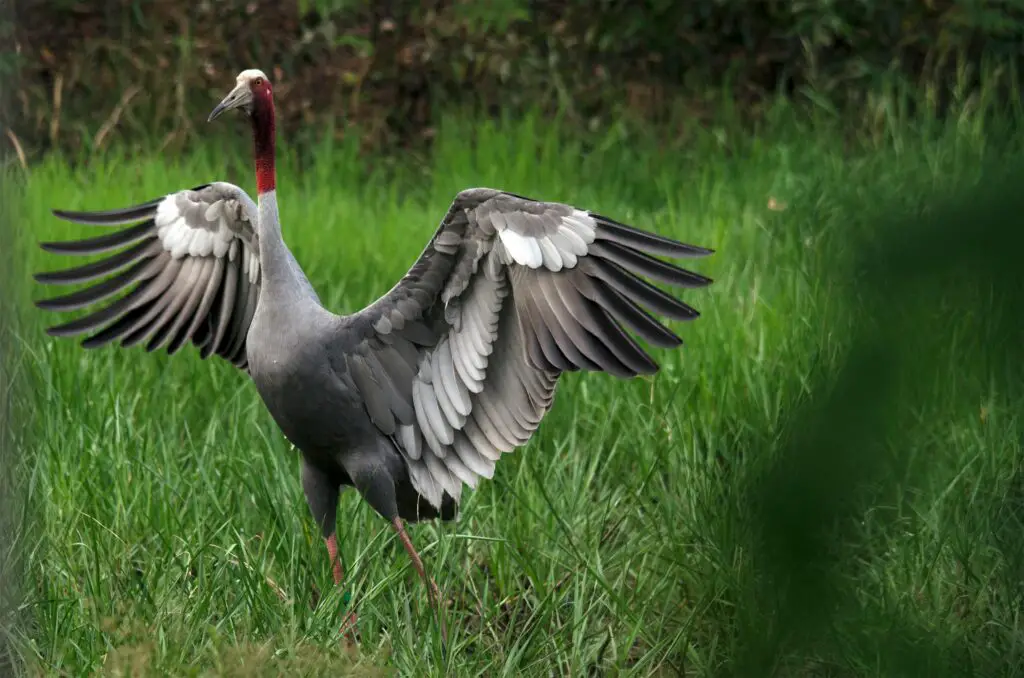
9. Sarus Crane – The World’s Tallest Flying Bird
- Average Height: 5.9–6 feet
- Average Weight: 15–26 pounds
- Habitat: Wetlands in South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Australia
With their long legs and graceful movements, Sarus cranes are known for their striking beauty and elaborate mating dances. These birds form lifelong bonds with their mates.

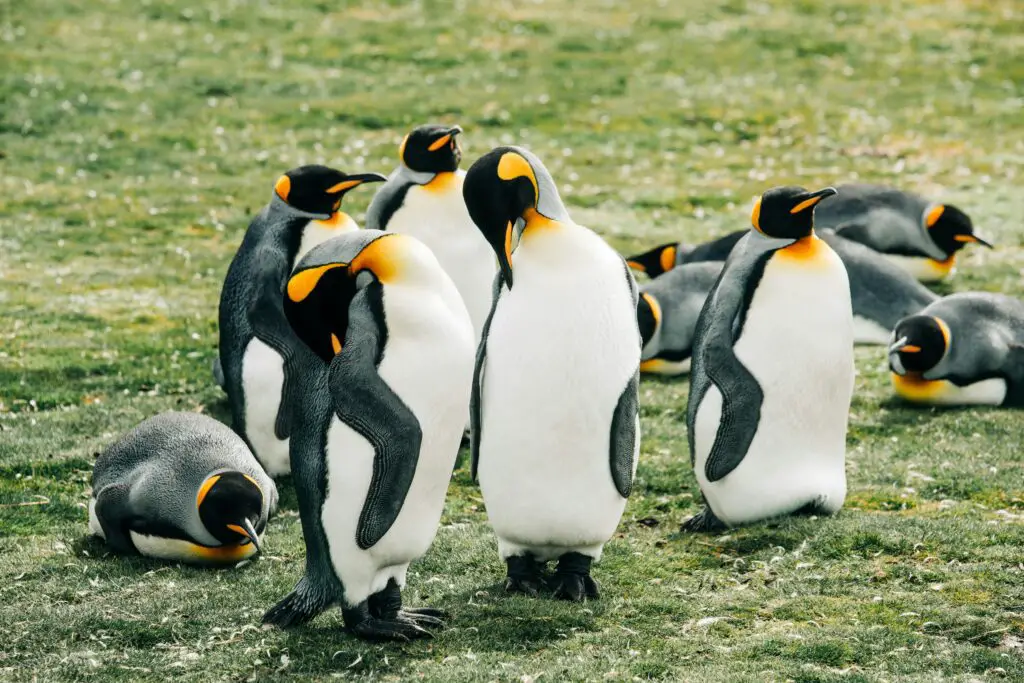
10. King Penguin – The Largest Penguin Species
- Average Height: 3.1–3.3 feet
- Average Weight: 25–35 pounds
- Habitat: Sub-Antarctic islands
King penguins are the second-largest penguin species after the emperor penguin. Their striking orange and yellow plumage make them one of the most recognizable birds in the world.

FAQs About Large Birds
What is the largest living bird?
The ostrich is the largest living bird, standing up to 9 feet tall and weighing up to 350 pounds.
Can the largest birds fly?
Most of the largest birds, like ostriches, cassowaries, and emus, are flightless. However, large flying birds like the wandering albatross and Dalmatian pelican excel at gliding or soaring.
Why are some birds flightless?
Flightless birds evolved in environments with fewer predators, prioritizing size and strength over the ability to fly.
Conclusion
The world of birds is full of surprises, and the largest ones truly stand out with their impressive size and unique adaptations. Whether it’s the sheer speed of an ostrich or the majestic flight of a wandering albatross, these birds remind us of nature’s incredible diversity.
If you ever get a chance to see one of these giants in the wild, take it—it’s an experience you won’t forget!
Animals
What is The Reason for Freshwater Fish Extinction?

Freshwater fish are an important part of the world’s ecosystems, providing food for both humans and other animals, as well as helping to control aquatic plant growth and maintain the balance of nutrients in their habitats. However, these valuable species are facing increasing threats, and many are at risk of extinction.
One of the main reasons for the decline in freshwater fish populations is habitat destruction. Human activities such as agriculture, urbanization, and the construction of dams and reservoirs have significantly altered and degraded the habitats of many fish species. As a result, these fish are losing their homes and are unable to find suitable places to live, reproduce, and thrive.
Another significant threat to freshwater fish is pollution. Industrial and agricultural runoff, as well as sewage and other forms of waste, can contaminate the water and make it inhospitable for fish. The use of chemicals such as pesticides and fertilizers can also have negative impacts on fish populations.
Overfishing is another major cause of freshwater fish extinction. Many species of fish, especially those that are economically valuable, are heavily targeted by commercial and recreational fishermen. This can lead to overfishing, which can deplete fish populations and make it difficult for them to recover.
Invasive species are also a significant threat to native fish populations. Non-native species, such as the Asian carp, can outcompete native fish for resources and habitat, leading to their decline. These invasive species can also introduce diseases and parasites that can spread to native fish and further harm their populations.
Climate change is another major factor that is contributing to the decline of freshwater fish populations. Rising water temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and other changes caused by climate change can have serious impacts on fish habitats and the species that depend on them.
In order to protect freshwater fish and prevent their extinction, it is important to address these various threats and take action to conserve these valuable species. This can include measures such as habitat restoration, pollution control, and sustainable fishing practices. It is also important to educate the public about the importance of freshwater fish and the threats they face so that more people can be involved in efforts to conserve these species.
Overall, the extinction of freshwater fish is a complex issue with many contributing factors. By understanding the reasons for their decline and taking action to address these issues, it is possible to protect these valuable species and ensure their continued survival.
Freshwater Fish Extinction
Freshwater fish can be found worldwide in various habitats, from small streams and ponds to large rivers and lakes. While many freshwater fish are harmless to humans, there are a few species that can pose a threat due to their size, venom, or aggressive behavior. Here are some of the most dangerous freshwater fish you should be aware of
Piranha
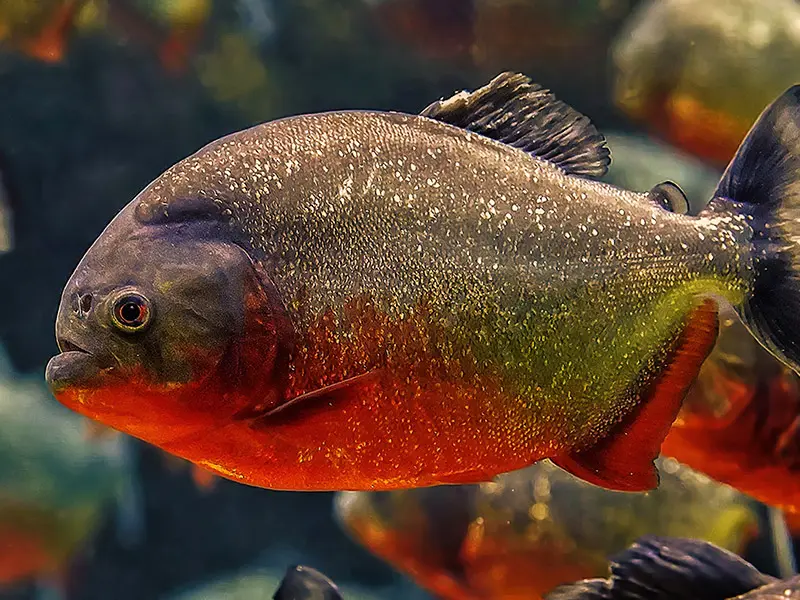
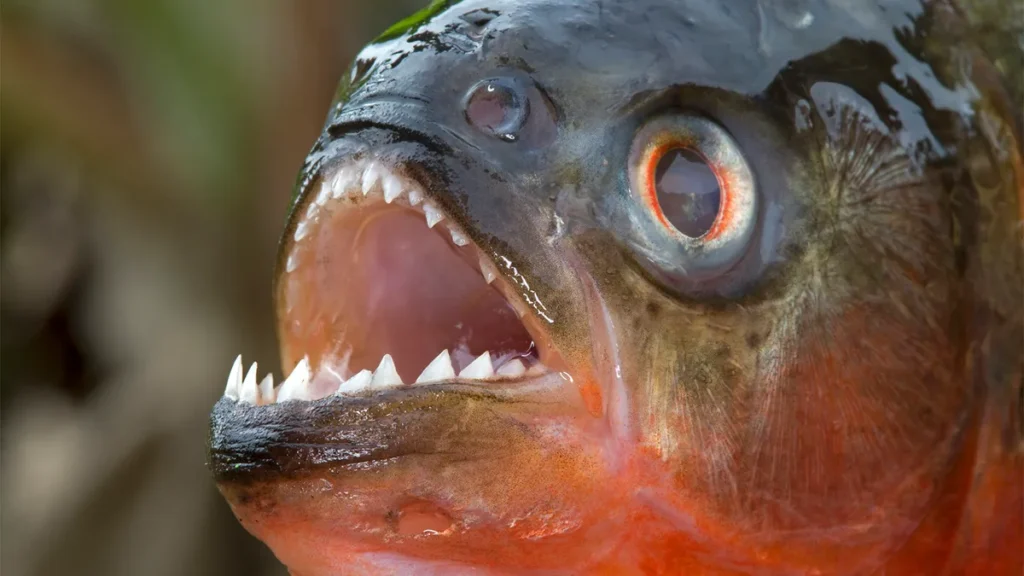
The piranha is perhaps the most well-known dangerous freshwater fish, thanks in part to its depiction in popular media as a ferocious predator. Found in the Amazon River and its tributaries in South America, piranhas are known for their sharp teeth and powerful jaws, which they use to feed on other fish, birds, and small mammals. While piranhas are not known to attack humans, they can be aggressive if provoked and have been known to bite people who accidentally step on them or try to handle them.


Electric eel
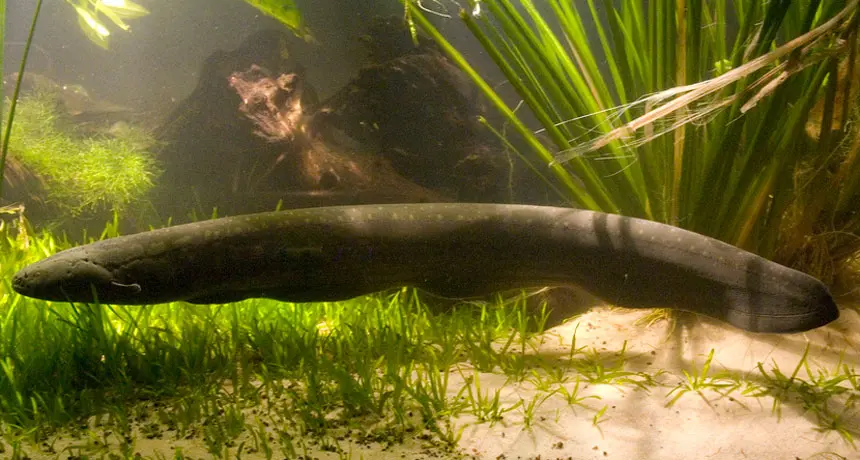
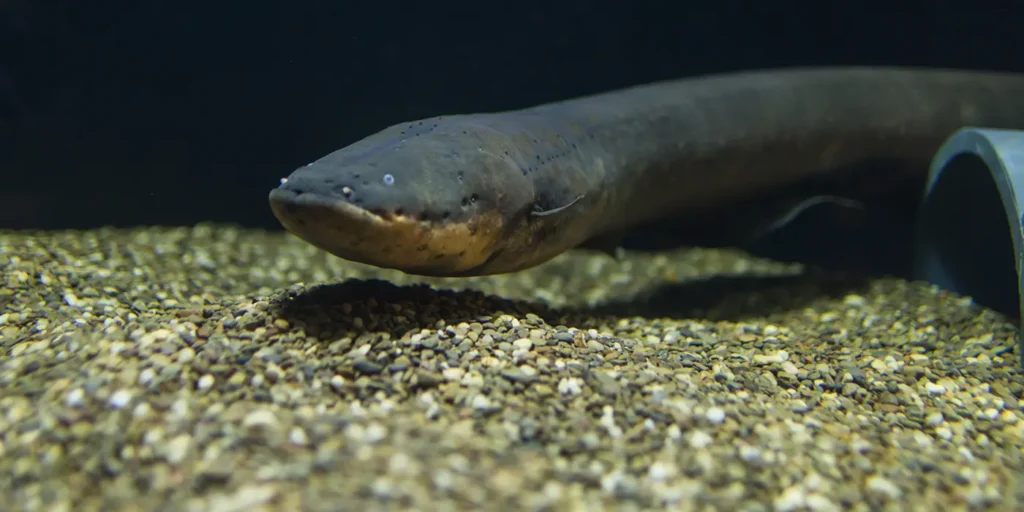
The electric eel is a species of knife fish found in the Amazon and Orinoco river basins in South America. It is not a true eel, but rather a type of fish that can generate powerful electric shocks as a defense mechanism. Electric eels can produce up to 600 volts of electricity, which is strong enough to stun or kill small prey. While electric eels are not known to attack humans, they can be dangerous if handled improperly, as the shock they produce can be strong enough to cause serious injury or death.


Alligator gar
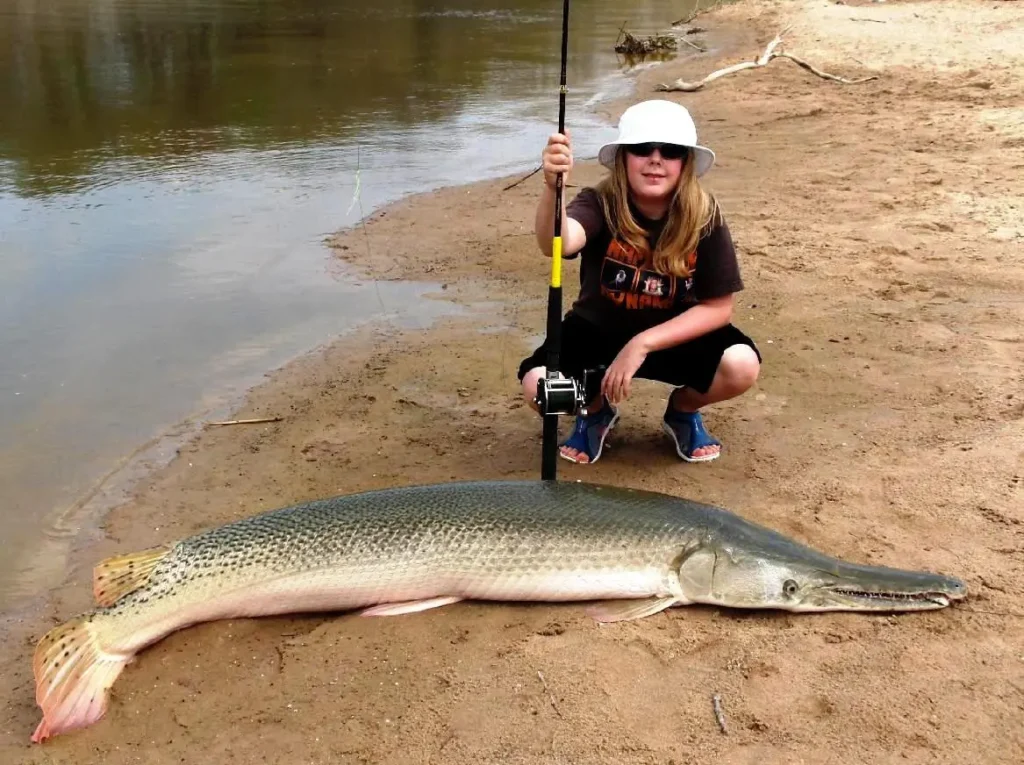
The alligator gar is a large, predatory fish found in the Mississippi River basin and the Gulf of Mexico. It is named for its long, narrow snout and sharp teeth, which resemble those of an alligator. Alligator gars can grow up to 10 feet in length and weigh over 300 pounds, making them one of the largest freshwater fish in North America. While they are not known to attack humans, they can be aggressive when caught, and their size and powerful jaws make them formidable predators.


Giant freshwater stingray
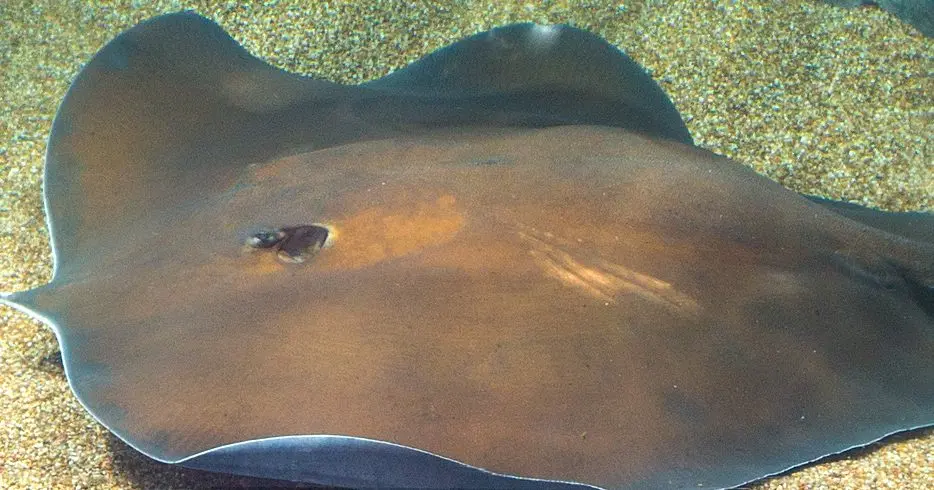
The giant freshwater stingray is a large species of stingray found in rivers and streams in Southeast Asia. It is known for its venomous stinger, which is located on the tail and can be used to defend itself against predators. The venom of the giant freshwater stingray can be harmful to humans, causing symptoms such as severe pain, swelling, and difficulty breathing. While attacks on humans are rare, it is important to be cautious when swimming or wading in areas where these fish are known to inhabit.

Pufferfish
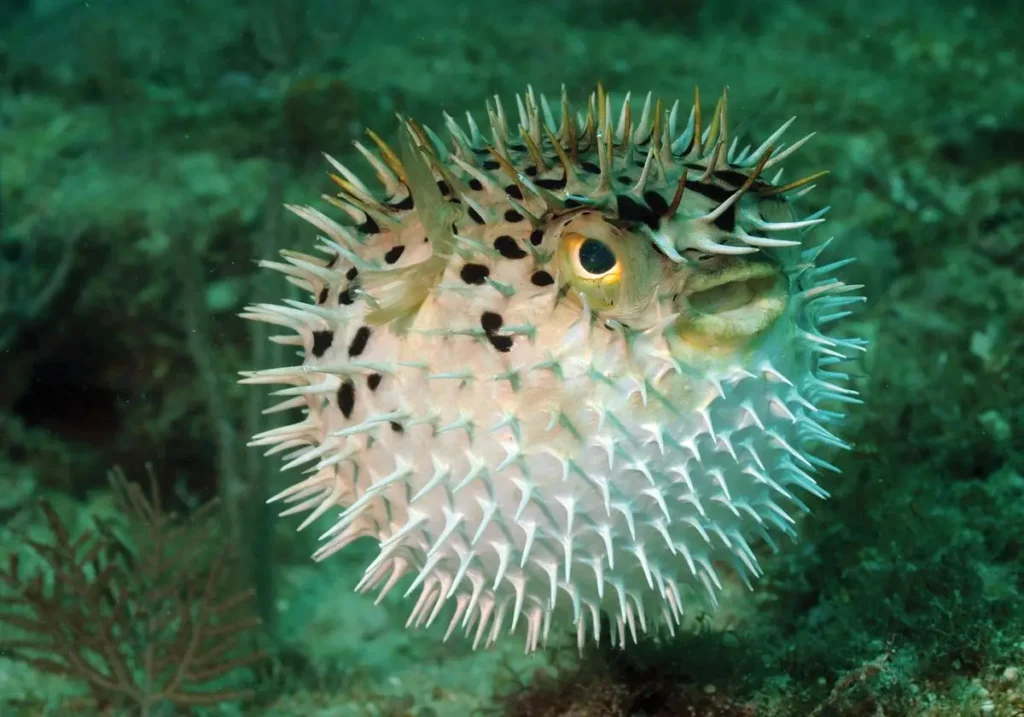
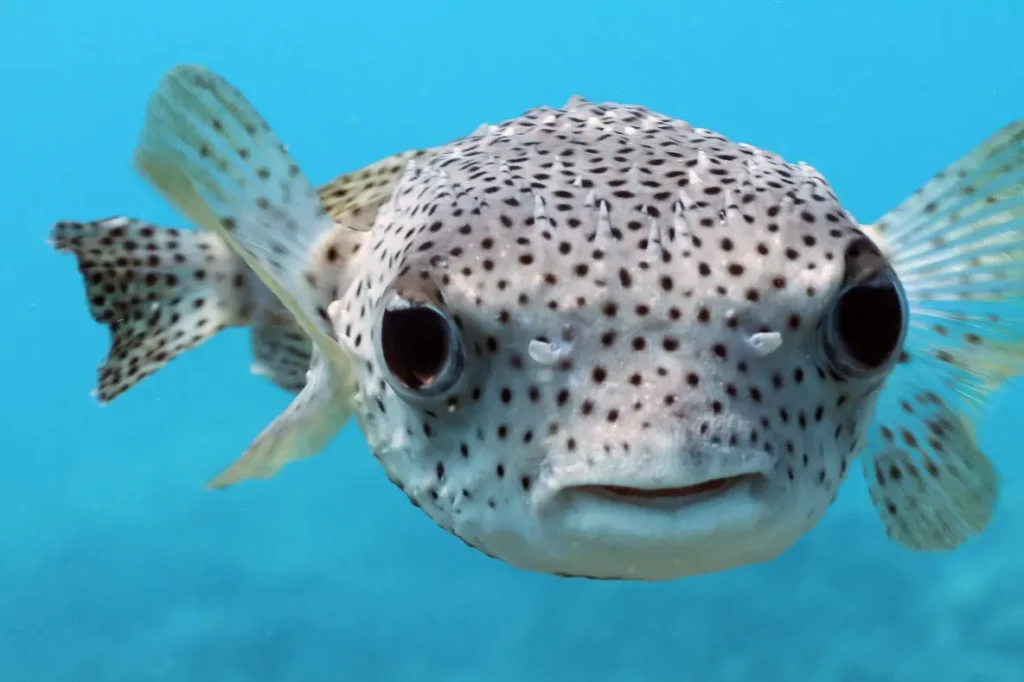
Pufferfish, also known as blowfish or fugu, are found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world. They are known for their ability to inflate their bodies by swallowing air or water when threatened, which makes them appear much larger and more formidable to predators. Pufferfish also contain a highly toxic substance called tetrodotoxin in their skin, liver, and gonads, which can be lethal to humans if ingested. While pufferfish are not aggressive, their venom can be dangerous if the fish is not prepared properly by a trained chef.


Conclusion
In conclusion, while most freshwater fish are harmless to humans, there are a few species that can pose a threat due to their size, venom, or aggressive behavior. It is important to be cautious and respect the natural environment when swimming or wading in areas where these fish are found. If you are unsure about the safety of a particular species, it is best to err on the side of caution and avoid handling or consuming it.
-

 Forests1 year ago
Forests1 year agoThe 10 Best Forests to Visit in the World
-

 Ocean1 year ago
Ocean1 year agoOceans in the World and Their Information & Locations
-

 Forests4 years ago
Forests4 years agoWhat Is The Biggest Rainforest In The World?
-

 Animals4 years ago
Animals4 years agoMost Popular Wild Animals in The World
-

 Animals4 years ago
Animals4 years ago(10) Insects Are Animals in the world?
-

 Forests1 year ago
Forests1 year agoThe Main Factors That Contribute to Forest Destruction
-

 Nature12 months ago
Nature12 months agoThe 10 Largest Farms in the World
-

 Plants and Trees4 years ago
Plants and Trees4 years agoBiggest Trees in The World List




